Page 77 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 77
Unit 4: Sampling Design
Suppose, 2,00,000 students are appearing for a competitive examination. We need to select 1% of Notes
them based on quota sampling. The classification of quota may be as follows:
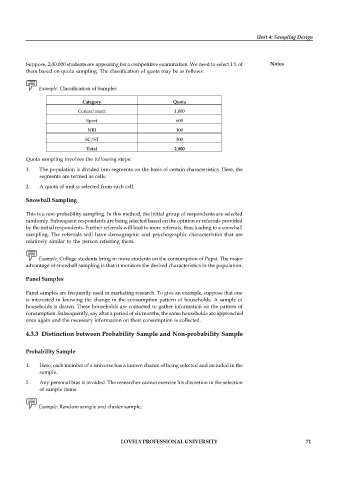
Example: Classification of Samples
Category Quota
General merit 1,000
Sport 600
NRI 100
SC/ST 300
Total 2,000
Quota sampling involves the following steps:
1. The population is divided into segments on the basis of certain characteristics. Here, the
segments are termed as cells.
2. A quota of unit is selected from each cell.
Snowball Sampling
This is a non-probability sampling. In this method, the initial group of respondents are selected
randomly. Subsequent respondents are being selected based on the opinion or referrals provided
by the initial respondents. Further referrals will lead to more referrals, thus leading to a snowball
sampling. The referrals will have demographic and psychographic characteristics that are
relatively similar to the person referring them.
Example: College students bring in more students on the consumption of Pepsi. The major
advantage of snowball sampling is that it monitors the desired characteristics in the population.
Panel Samples
Panel samples are frequently used in marketing research. To give an example, suppose that one
is interested in knowing the change in the consumption pattern of households. A sample of
households is drawn. These households are contacted to gather information on the pattern of
consumption. Subsequently, say after a period of six months, the same households are approached
once again and the necessary information on their consumption is collected.
4.3.3 Distinction between Probability Sample and Non-probability Sample
Probability Sample
1. Here, each member of a universe has a known chance of being selected and included in the
sample.
2. Any personal bias is avoided. The researcher cannot exercise his discretion in the selection
of sample items.
Example: Random sample and cluster sample.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 71