Page 264 - DCOM506_DMGT502_STRATEGIC_MANAGEMENT
P. 264
Strategic Management
Notes
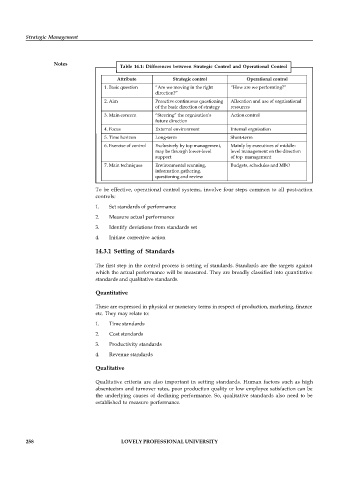
Table 14.1: Differences between Strategic Control and Operational Control
Attribute Strategic control Operational control
1. Basic question “Are we moving in the right “How are we performing?”
direction?”
2. Aim Proactive continuous questioning Allocation and use of orgnisational
of the basic direction of strategy resources
3. Main concern “Steering” the orgnisation’s Action control
future direction
4. Focus External environment Internal orgnisation
5. Time horizon Long-term Short-term
6. Exercise of control Exclusively by top management, Mainly by executives of middle-
may be through lower-level level management on the direction
support of top management
7. Main techniques Environmental scanning, Budgets, schedules and MBO
information gathering,
questioning and review
To be effective, operational control systems, involve four steps common to all post-action
controls:
1. Set standards of performance
2. Measure actual performance
3. Identify deviations from standards set
4. Initiate corrective action
14.3.1 Setting of Standards
The first step in the control process is setting of standards. Standards are the targets against
which the actual performance will be measured. They are broadly classified into quantitative
standards and qualitative standards.
Quantitative
These are expressed in physical or monetary terms in respect of production, marketing, finance
etc. They may relate to:
1. Time standards
2. Cost standards
3. Productivity standards
4. Revenue standards
Qualitative
Qualitative criteria are also important in setting standards. Human factors such as high
absenteeism and turnover rates, poor production quality or low employee satisfaction can be
the underlying causes of declining performance. So, qualitative standards also need to be
established to measure performance.
258 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY