Page 237 - DCOM507_STOCK_MARKET_OPERATIONS
P. 237
Stock Market Operations
Notes Introduction
Various authors have defined a mutual fund in different ways. According to Pierce, James L, it is
a non-depository or non-banking financial intermediary which acts as an “important vehicle for
bringing wealth holders and deficit units together directly.”
Weston, J. Fred and Brigham, Eugene F, in their book Essentials of Managerial Finance state that
mutual funds are corporations that accept dollars from savers and then use these dollars to buy
stock, long-term bonds, short-term debt instruments issued by business or government. These
corporations pool funds and thus reduce risk by diversification.
A mutual fund is essentially a mechanism of pooling together the savings of a large number of
small investors for collective investment, with an avowed objective of attractive yields and
capital appreciation, holding the safety and liquidity as prime parameters.
According to the author:
A mutual fund is a trust that pools the savings of a number of investors who share a common
financial goal. The money, thus, collected is then invested in capital market instruments such as
shares, debentures and other securities. The income earned through these investments and the
capital appreciation realised are shared by its unit holders in proportion to the number of units
owned by them. Thus, a mutual fund is the most suitable investment for the common man as it
offers an opportunity to invest in a diversified, professionally managed basket of securities at a
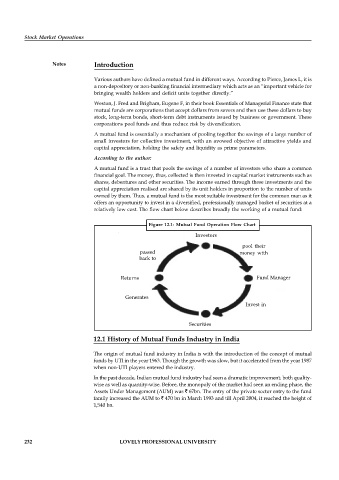
relatively low cost. The flow chart below describes broadly the working of a mutual fund:
Figure 12.1: Mutual Fund Operation Flow Chart
Investors
pool their
passed money with
back to
Returns Fund Manager
Generates
Invest in
Securities
12.1 History of Mutual Funds Industry in India
The origin of mutual fund industry in India is with the introduction of the concept of mutual
funds by UTI in the year 1963. Though the growth was slow, but it accelerated from the year 1987
when non-UTI players entered the industry.
In the past decade, Indian mutual fund industry had seen a dramatic improvement, both quality-
wise as well as quantity-wise. Before, the monopoly of the market had seen an ending phase, the
Assets Under Management (AUM) was ` 67bn. The entry of the private sector entry to the fund
family increased the AUM to ` 470 bn in March 1993 and till April 2004, it reached the height of
1,540 bn.
232 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY