Page 240 - DCOM507_STOCK_MARKET_OPERATIONS
P. 240
Unit 12: Mutual Fund
Indeed there is. Combing through annual performance data instead of rolling year periods, Notes
we find that this fund actually outperformed handily for the first 9 full years of its existence,
beating the benchmark in 7 of those 9 years. In fact, they beat the benchmark in 8 of 12 or
two-thirds of the full calendar years available, which is normally an impressive feat. The
table, in this SEC required format, is highly misleading in terms of the accomplishments
of this fund. Despite the good intentions of standardized performance reporting (which I
still applaud), it certainly does not present an accurate picture in all cases. One lesson here
is that investors who don’t look deeper will often miss the larger picture.
Source: http://thelongrunblog.wordpress.com/2011/04/14/mutual-fund-perf/
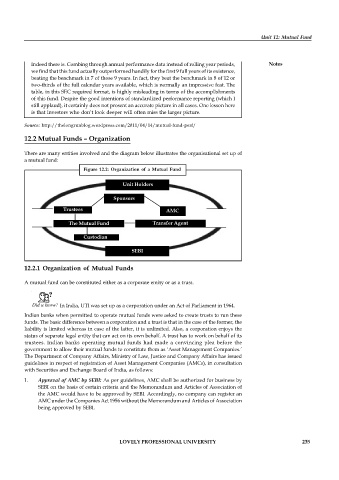
12.2 Mutual Funds – Organization
There are many entities involved and the diagram below illustrates the organisational set up of
a mutual fund:
Figure 12.2: Organization of a Mutual Fund
Unit Holders
Sponsors
Trustees AMC
The Mutual Fund Transfer Agent
Custodian
SEBI
12.2.1 Organization of Mutual Funds
A mutual fund can be constituted either as a corporate entity or as a trust.
Did u know? In India, UTI was set up as a corporation under an Act of Parliament in 1964.
Indian banks when permitted to operate mutual funds were asked to create trusts to run these
funds. The basic difference between a corporation and a trust is that in the case of the former, the
liability is limited whereas in case of the latter, it is unlimited. Also, a corporation enjoys the
status of separate legal entity that can act on its own behalf. A trust has to work on behalf of its
trustees. Indian banks operating mutual funds had made a convincing plea before the
government to allow their mutual funds to constitute them as ‘Asset Management Companies.’
The Department of Company Affairs, Ministry of Law, Justice and Company Affairs has issued
guidelines in respect of registration of Asset Management Companies (AMCs), in consultation
with Securities and Exchange Board of India, as follows:
1. Approval of AMC by SEBI: As per guidelines, AMC shall be authorized for business by
SEBI on the basis of certain criteria and the Memorandum and Articles of Association of
the AMC would have to be approved by SEBI. Accordingly, no company can register an
AMC under the Companies Act 1956 without the Memorandum and Articles of Association
being approved by SEBI.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 235