Page 55 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 55
Digital Circuits and Logic Design
Notes
z = (A + C ) + (B + D )
= (AC• ) + BD
•
Here we have broken the larger, inverter signs down the middle and replaced the (+) with
a(•). Cancelling out the double inversions, we have finally
z = AC + BD
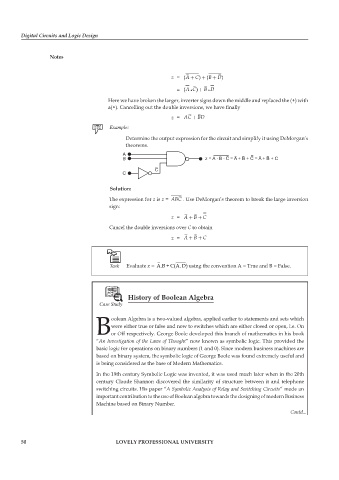
Determine the output expression for the circuit and simplify it using DeMorgan’s
theorems.
Solution:
The expression for z is z = ABC . Use DeMorgan’s theorem to break the large inversion
sign:
z = A + B + C
Cancel the double inversions over C to obtain
z = A + B + C
Evaluate x = A.B+ C(A. D) using the convention A = True and B = False.
History of Boolean Algebra
oolean Algebra is a two-valued algebra, applied earlier to statements and sets which
were either true or false and now to switches which are either closed or open, i.e. On
Bor Off respectively. George Boole developed this branch of mathematics in his book
“An Investigation of the Laws of Thought” now known as symbolic logic. This provided the
basic logic for operations on binary numbers (1 and 0). Since modern business machines are
based on binary system, the symbolic logic of George Boole was found extremely useful and
is being considered as the base of Modern Mathematics.
In the 19th century Symbolic Logic was invented, it was used much later when in the 20th
century Claude Shannon discovered the similarity of structure between it and telephone
switching circuits. His paper “A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits” made an
important contribution to the use of Boolean algebra towards the designing of modern Business
Machine based on Binary Number.
Contd...
50 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY