Page 195 - DCAP310_INTRODUCTION_TO_ARTIFICIAL_INTELLIGENCE_AND_EXPERT_SYSTEMS
P. 195
Unit 10: Matching Techniques
Symbolic entities can be introduced to represent many different classes of relevant features of a Notes
string. For instance,
StringExpression[LetterCharacter, DigitCharacter]
will match a string that consists of a letter first, and then a number.
Guards could be used to achieve the same matches:
[letter, digit] | isAlpha letter && isDigit digit
The main advantage of symbolic string manipulation is that it can be completely integrated
with the rest of the programming language, rather than being a separate, special purpose subunit.
The entire power of the language can be leveraged to build up the patterns themselves or
analyze and transform the programs that contain them.
!
Caution Use of pattern matching carefully.
Task Learn the working of character recognition from several websites.
Self Assessment
State whether the following statements are true or false:
4. Strings are not represented as trees of root String Expression.
5. The function Trace can be used to monitor a computation, and return the elements that
arise which match a pattern.
6. In Mathematica, some structure that exists is the tree, which is populated by symbols.
10.3 Matching Like Patterns
The pattern-matching conditions compare character data.
LIKE Condition
The LIKE conditions specify a test involving pattern matching. Whereas the equality operator
(=) exactly matches one character value to another, the LIKE conditions match a portion of one
character value to another by searching the first value for the pattern specified by the second.
LIKE calculates strings using characters as defined by the input character set. LIKEC uses Unicode
complete characters. LIKE2 uses UCS2 code points. LIKE4 uses UCS4 code points.
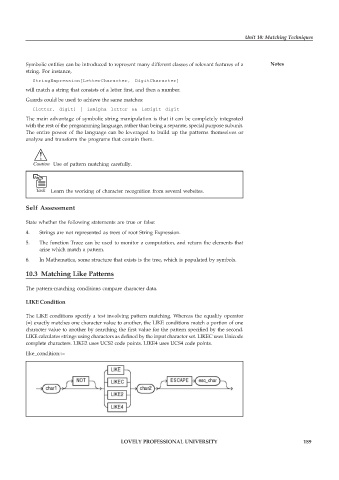
like_condition::=
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 189