Page 153 - DCAP516_COMPUTER_SECURITY
P. 153
Unit 12: Network Security Controls
(ii) malicious or non-malicious modification that changes content in a way that is not Notes
necessarily meaningful
(iii) non-malicious modification that changes content in a way that will not be detected
(iv) Encryption addresses the first of these threats very effectively. To address the others,
we can use other controls.
8. Error Correcting Codes: We can use error detection and error correction codes to guard
against modification in a transmission. The codes work as their names imply: Error
detection codes detect when an error has occurred, and error correction codes can actually
correct errors without requiring retransmission of the original message. The error code is
transmitted along with the original data, so the recipient can recompute the error code
and check whether the received result matches the expected value.
Task Name different types of error detection and error correction techniques.
9. Firewalls: A firewall is designed to do the screening that is less appropriate for a router to
do. A router’s primary function is addressing, whereas a firewall’s primary function is
filtering. Firewalls can also do auditing. Even more important, firewalls can examine an
entire packet’s contents, including the data portion, whereas a router is concerned only
with source and destination MAC and IP addresses. Because they are an extremely important
network security control, we will study firewalls in the next unit.
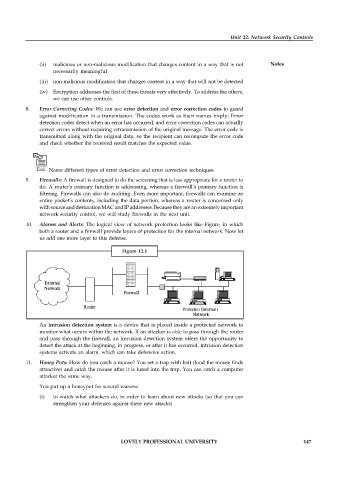
10. Alarms and Alerts: The logical view of network protection looks like Figure, in which
both a router and a firewall provide layers of protection for the internal network. Now let
us add one more layer to this defense.
Figure 12.1
An intrusion detection system is a device that is placed inside a protected network to
monitor what occurs within the network. If an attacker is able to pass through the router
and pass through the firewall, an intrusion detection system offers the opportunity to
detect the attack at the beginning, in progress, or after it has occurred. Intrusion detection
systems activate an alarm, which can take defensive action.
11. Honey Pots: How do you catch a mouse? You set a trap with bait (food the mouse finds
attractive) and catch the mouse after it is lured into the trap. You can catch a computer
attacker the same way.
You put up a honeypot for several reasons:
(i) to watch what attackers do, in order to learn about new attacks (so that you can
strengthen your defenses against these new attacks)
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 147