Page 189 - DCAP516_COMPUTER_SECURITY
P. 189
Unit 14: Intrusion Detection System and Secure E-mail
2. Asymmetric PGP: The key used for encryption and decryption is different. Keys come in Notes
pairs - public (known to all) and private. Which everybody has? Usually encryption is
done using public key so that the private key is used for decryption by the receiver only
for which the message is meant.
Example of Asymmetric PGP is RSA .
Symmetric is usually faster as compared to asymmetric. In asymmetric PGP there is a problem
of key distribution. A hash function is applied on every message so that no two messages hash
to the same value. Now the hash function is encrypted. If the hash function of source and
destination matches then No tampering. If the key for encryption is private then not everybody
can generate the message although anyone can read it. So this scheme lacks privacy tackles the
other security issues.
Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM)
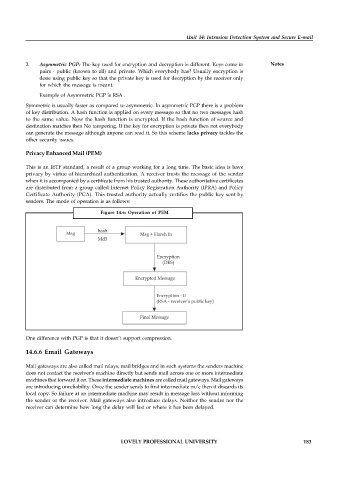
This is an IETF standard, a result of a group working for a long time. The basic idea is have
privacy by virtue of hierarchical authentication. A receiver trusts the message of the sender
when it is accompanied by a certificate from his trusted authority. These authoritative certificates
are distributed from a group called Internet Policy Registration Authority (IPRA) and Policy
Certificate Authority (PCA). This trusted authority actually certifies the public key sent by
senders. The mode of operation is as follows:
Figure 14.6: Operation of PEM
One difference with PGP is that it doesn’t support compression.
14.6.6 Email Gateways
Mail gateways are also called mail relays, mail bridges and in such systems the senders machine
does not contact the receiver’s machine directly but sends mail across one or more intermediate
machines that forward it on. These intermediate machines are called mail gateways. Mail gateways
are introducing unreliability. Once the sender sends to first intermediate m/c then it discards its
local copy. So failure at an intermediate machine may result in message loss without informing
the sender or the receiver. Mail gateways also introduce delays. Neither the sender nor the
receiver can determine how long the delay will last or where it has been delayed.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 183