Page 11 - DMGT106_MANAGING_HUMAN_ELEMENTS_AT_WORK
P. 11
Unit 1: Introduction to Human Resource Management
Notes
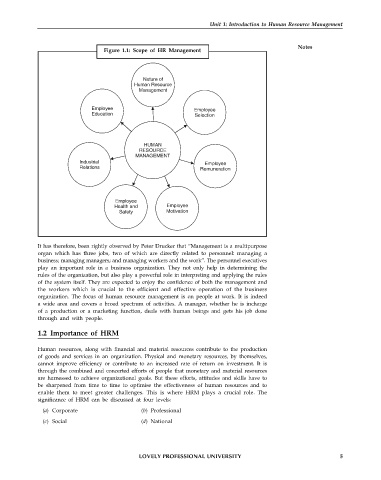
Figure 1.1: Scope of HR Management
Nature of
Human Resource
Management
Employee Employee
Education Selection
HUMAN
RESOURCE
MANAGEMENT
Industrial Employee
Relations Remuneration
Employee
Health and Employee
Safety Motivation
It has therefore, been rightly observed by Peter Drucker that “Management is a multipurpose
organ which has three jobs, two of which are directly related to personnel: managing a
business; managing managers; and managing workers and the work”. The personnel executives
play an important role in a business organization. They not only help in determining the
rules of the organization, but also play a powerful role in interpreting and applying the rules
of the system itself. They are expected to enjoy the confidence of both the management and
the workers which is crucial to the efficient and effective operation of the business
organization. The focus of human resource management is on people at work. It is indeed
a wide area and covers a broad spectrum of activities. A manager, whether he is incharge
of a production or a marketing function, deals with human beings and gets his job done
through and with people.
1.2 Importance of HRM
Human resources, along with financial and material resources contribute to the production
of goods and services in an organization. Physical and monetary resources, by themselves,
cannot improve efficiency or contribute to an increased rate of return on investment. It is
through the combined and concerted efforts of people that monetary and material resources
are harnessed to achieve organizational goals. But these efforts, attitudes and skills have to
be sharpened from time to time to optimise the effectiveness of human resources and to
enable them to meet greater challenges. This is where HRM plays a crucial role. The
significance of HRM can be discussed at four levels:
(a) Corporate (b) Professional
(c) Social (d) National
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 5