Page 27 - DCAP208_Management Support Systems
P. 27
Management Support Systems
Notes of nature that can be described in units of monetary value. The units of monetary value are also
described as conditional values.
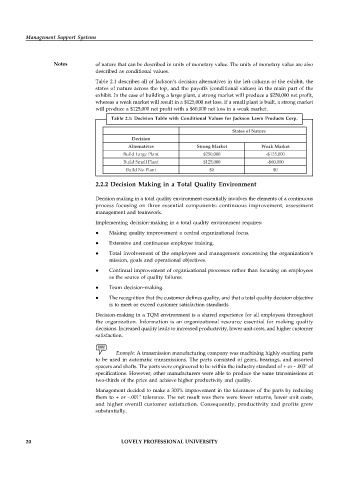
Table 2.1 describes all of Jackson‘s decision alternatives in the left column of the exhibit, the
states of nature across the top, and the payoffs (conditional values) in the main part of the
exhibit. In the case of building a large plant, a strong market will produce a $250,000 net profit,
whereas a weak market will result in a $125,000 net loss. If a small plant is built, a strong market
will produce a $125,000 net profit with a $60,000 net loss in a weak market.
Table 2.1: Decision Table with Conditional Values for Jackson Lawn Products Corp.
States of Nature
Decision
Alternatives Strong Market Weak Market
Build Large Plant $250,000 -$125,000
Build Small Plant $125,000 -$60,000
Build No Plant $0 $0
2.2.2 Decision Making in a Total Quality Environment
Decision making in a total quality environment essentially involves the elements of a continuous
process focusing on three essential components: continuous improvement, assessment
management and teamwork.
Implementing decision-making in a total quality environment requires:
Making quality improvement a central organizational focus.
Extensive and continuous employee training.
Total involvement of the employees and management concerning the organization‘s
mission, goals and operational objectives.
Continual improvement of organizational processes rather than focusing on employees
as the source of quality failures.
Team decision-making.
The recognition that the customer defines quality, and that a total quality decision objective
is to meet or exceed customer satisfaction standards.
Decision-making in a TQM environment is a shared experience for all employees throughout
the organization. Information is an organizational resource essential for making quality
decisions. Increased quality leads to increased productivity, lower unit costs, and higher customer
satisfaction.
Example: A transmission manufacturing company was machining highly exacting parts
to be used in automatic transmissions. The parts consisted of gears, bearings, and assorted
spacers and shafts. The parts were engineered to be within the industry standard of + or - .003" of
specifications. However, other manufacturers were able to produce the same transmissions at
two-thirds of the price and achieve higher productivity and quality.
Management decided to make a 300% improvement in the tolerances of the parts by reducing
them to + or –.001" tolerance. The net result was there were fewer returns, lower unit costs,
and higher overall customer satisfaction. Consequently, productivity and profits grew
substantially.
20 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY