Page 209 - DCAP304_DCAP515_SOFTWARE_PROJECT_MANAGEMENT
P. 209
Unit 10: Risk Management
10.10 PERT Technique Notes
A PERT chart is a project management tool used to schedule, organize, and coordinate tasks
within a project. PERT stands for Program Evaluation Review Technique, a methodology developed
by the U.S. Navy in the 1950s to manage the Polaris submarine missile program. A similar
methodology, the Critical Path Method (CPM) was developed for project management in the
private sector at about the same time.
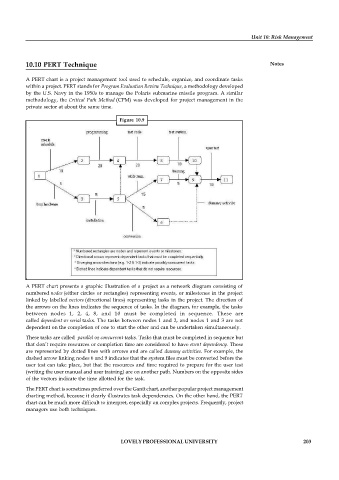
Figure 10.9
A PERT chart presents a graphic illustration of a project as a network diagram consisting of
numbered nodes (either circles or rectangles) representing events, or milestones in the project
linked by labelled vectors (directional lines) representing tasks in the project. The direction of
the arrows on the lines indicates the sequence of tasks. In the diagram, for example, the tasks
between nodes 1, 2, 4, 8, and 10 must be completed in sequence. These are
called dependent or serial tasks. The tasks between nodes 1 and 2, and nodes 1 and 3 are not
dependent on the completion of one to start the other and can be undertaken simultaneously.
These tasks are called parallel or concurrent tasks. Tasks that must be completed in sequence but
that don’t require resources or completion time are considered to have event dependency. These
are represented by dotted lines with arrows and are called dummy activities. For example, the
dashed arrow linking nodes 6 and 9 indicates that the system files must be converted before the
user test can take place, but that the resources and time required to prepare for the user test
(writing the user manual and user training) are on another path. Numbers on the opposite sides
of the vectors indicate the time allotted for the task.
The PERT chart is sometimes preferred over the Gantt chart, another popular project management
charting method, because it clearly illustrates task dependencies. On the other hand, the PERT
chart can be much more difficult to interpret, especially on complex projects. Frequently, project
managers use both techniques.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 203