Page 84 - DCAP306_DCAP511_E-COMMERCE_AND_E-BUSINESS
P. 84
Unit 6: Security Framework
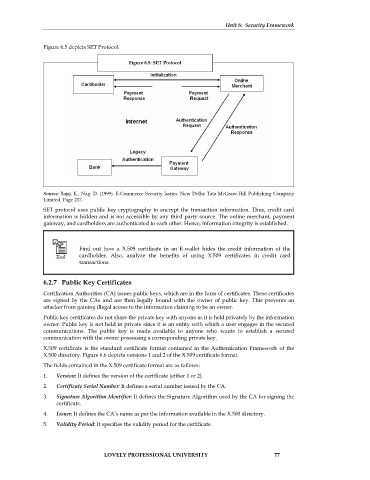
Figure 6.5 depicts SET Protocol.
Figure 6.5: SET Protocol
Source: Bajaj. K., Nag. D. (1999). E-Commerce Security Issues. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company
Limited. Page 217.
SET protocol uses public key cryptography to encrypt the transaction information. Thus, credit card
information is hidden and is not accessible by any third party source. The online merchant, payment
gateway, and cardholders are authenticated to each other. Hence, information integrity is established.
Find out how a X.509 certificate in an E-wallet hides the credit information of the
cardholder. Also, analyze the benefits of using X.509 certificates in credit card
transactions.
6.2.7 Public Key Certificates
Certification Authorities (CA) issues public keys, which are in the form of certificates. These certificates
are signed by the CAs and are then legally bound with the owner of public key. This prevents an
attacker from gaining illegal access to the information claiming to be an owner.
Public key certificates do not share the private key with anyone as it is held privately by the information
owner. Public key is not held in private since it is an entity with which a user engages in the secured
communications. The public key is made available to anyone who wants to establish a secured
communication with the owner possessing a corresponding private key.
X.509 certificate is the standard certificate format contained in the Authentication Framework of the
X.500 directory. Figure 6.6 depicts versions 1 and 2 of the X.509 certificate format.
The fields contained in the X.509 certificate format are as follows:
1. Version: It defines the version of the certificate (either 1 or 2).
2. Certificate Serial Number: It defines a serial number issued by the CA.
3. Signature Algorithm Identifier: It defines the Signature Algorithm used by the CA for signing the
certificate.
4. Issuer: It defines the CA’s name as per the information available in the X.500 directory.
5. Validity Period: It specifies the validity period for the certificate.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 77