Page 73 - DCAP307_PLANNING_AND_MANAGING_IT_INFRASTRUCTURE
P. 73
Unit 4: Business Process and IT Outsourcing
liabilities, negative impact on business partner and customer relationships and satisfaction, and Notes
potential data and security breaches.
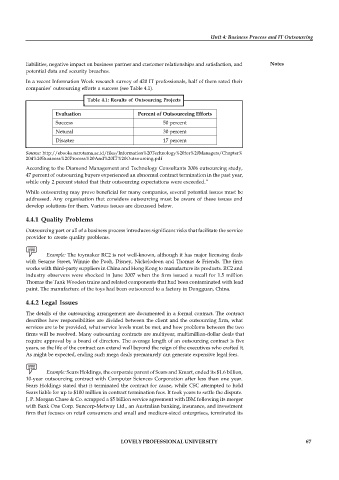
In a recent Information Week research survey of 420 IT professionals, half of them rated their
companies’ outsourcing efforts a success (see Table 4.1).
Table 4.1: Results of Outsourcing Projects
Evaluation Percent of Outsourceing Efforts
Success 50 percent
Netural 30 percent
Disaster 17 percent
Source: http://ebooks.narotama.ac.id/files/Information%20Technology%20for%20Managers/Chapter%
204%20Business%20Process%20And%20IT%20Outsourcing.pdf
According to the Diamond Management and Technology Consultants 2006 outsourcing study,
47 percent of outsourcing buyers experienced an abnormal contract termination in the past year,
while only 2 percent stated that their outsourcing expectations were exceeded.”
While outsourcing may prove beneficial for many companies, several potential issues must be
addressed. Any organisation that considers outsourcing must be aware of these issues and
develop solutions for them. Various issues are discussed below.
4.4.1 Quality Problems
Outsourcing part or all of a business process introduces significant risks that facilitate the service
provider to create quality problems.
Example: The toymaker RC2 is not well-known, although it has major licensing deals
with Sesame Street, Winnie the Pooh, Disney, Nickelodeon and Thomas & Friends. The firm
works with third-party suppliers in China and Hong Kong to manufacture its products. RC2 and
industry observers were shocked in June 2007 when the firm issued a recall for 1.5 million
Thomas the Tank Wooden trains and related components that had been contaminated with lead
paint. The manufacture of the toys had been outsourced to a factory in Dongguan, China.
4.4.2 Legal Issues
The details of the outsourcing arrangement are documented in a formal contract. The contract
describes how responsibilities are divided between the client and the outsourcing firm, what
services are to be provided, what service levels must be met, and how problems between the two
firms will be resolved. Many outsourcing contracts are multiyear, multimillion-dollar deals that
require approval by a board of directors. The average length of an outsourcing contract is five
years, so the life of the contract can extend well beyond the reign of the executives who crafted it.
As might be expected, ending such mega deals prematurely can generate expensive legal fees.
Example: Sears Holdings, the corporate parent of Sears and Kmart, ended its $1.6 billion,
10-year outsourcing contract with Computer Sciences Corporation after less than one year.
Sears Holdings stated that it terminated the contract for cause, while CSC attempted to hold
Sears liable for up to $100 million in contract termination fees. It took years to settle the dispute.
J. P. Morgan Chase & Co. scrapped a $5 billion service agreement with IBM following its merger
with Bank One Corp. Suncorp-Metway Ltd., an Australian banking, insurance, and investment
firm that focuses on retail consumers and small and medium-sized enterprises, terminated its
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 67