Page 246 - DCAP103_Principle of operating system
P. 246
Unit 7: Secondary Storage Structure
Notes
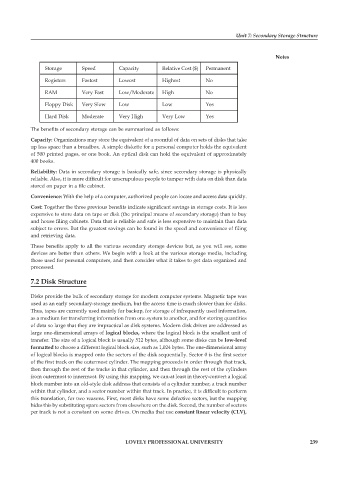
Storage Speed Capacity Relative Cost ($) Permanent
Registers Fastest Lowest Highest No
RAM Very Fast Low/Moderate High No
Floppy Disk Very Slow Low Low Yes
Hard Disk Moderate Very High Very Low Yes
The benefits of secondary storage can be summarized as follows:
Capacity: Organizations may store the equivalent of a roomful of data on sets of disks that take
up less space than a breadbox. A simple diskette for a personal computer holds the equivalent
of 500 printed pages, or one book. An optical disk can hold the equivalent of approximately
400 books.
Reliability: Data in secondary storage is basically safe, since secondary storage is physically
reliable. Also, it is more difficult for unscrupulous people to tamper with data on disk than data
stored on paper in a file cabinet.
Convenience: With the help of a computer, authorized people can locate and access data quickly.
Cost: Together the three previous benefits indicate significant savings in storage costs. It is less
expensive to store data on tape or disk (the principal means of secondary storage) than to buy
and house filing cabinets. Data that is reliable and safe is less expensive to maintain than data
subject to errors. But the greatest savings can be found in the speed and convenience of filing
and retrieving data.
These benefits apply to all the various secondary storage devices but, as you will see, some
devices are better than others. We begin with a look at the various storage media, including
those used for personal computers, and then consider what it takes to get data organized and
processed.
7.2 Disk Structure
Disks provide the bulk of secondary storage for modern computer systems. Magnetic tape was
used as an early secondary-storage medium, but the access time is much slower than for disks.
Thus, tapes are currently used mainly for backup, for storage of infrequently used information,
as a medium for transferring information from one system to another, and for storing quantities
of data so large that they are impractical as disk systems. Modern disk drives are addressed as
large one-dimensional arrays of logical blocks, where the logical block is the smallest unit of
transfer. The size of a logical block is usually 512 bytes, although some disks can be low-level
formatted to choose a different logical block size, such as 1,024 bytes. The one-dimensional array
of logical blocks is mapped onto the sectors of the disk sequentially. Sector 0 is the first sector
of the first track on the outermost cylinder. The mapping proceeds in order through that track,
then through the rest of the tracks in that cylinder, and then through the rest of the cylinders
from outermost to innermost. By using this mapping, we can-at least in theory-convert a logical
block number into an old-style disk address that consists of a cylinder number, a track number
within that cylinder, and a sector number within that track. In practice, it is difficult to perform
this translation, for two reasons. First, most disks have some defective sectors, but the mapping
hides this by substituting spare sectors from elsewhere on the disk. Second, the number of sectors
per track is not a constant on some drives. On media that use constant linear velocity (CLV),
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 239