Page 250 - DCAP103_Principle of operating system
P. 250
Unit 7: Secondary Storage Structure
3. Which of the following disk scheduling techniques has a drawback of starvation? Notes
(a) SCAN (b) SST
(c) FCFS (d) LIFO
4. The total time to prepare a disk drive mechanism for a block of data to be read from is
its
(a) latency
(b) latency plus transmission time
(c) latency plus seek time
(d) latency plus seek time plus transmission time
7.4 Selecting a Disk Scheduling Algorithm
The performance of these algorithms depends heavily on the workload (number of requests).
Under light load all algorithms perform the same. If the queue seldom has more than one
outstanding request, then all algorithms are effectively the same. Their performance also depends
upon the file organization and the type of generated requests. In a sequential processing and
sequential file, the head movement will be minimum and therefore the seek time and latency
time will be minimum so FCFS may perform better. A indexed sequential file, on the other hand,
may include blocks that may be scattered all over the disk and a sequential processing with
FCFS will be very slow. SSTF is quite common and scan and cscan are good for heavy load.
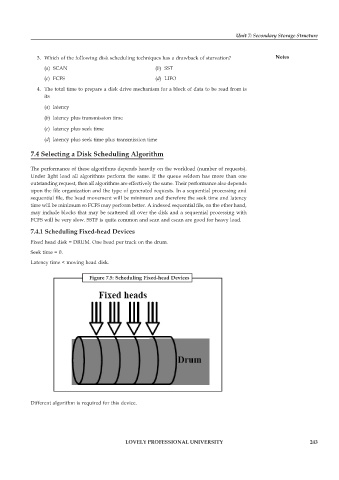
7.4.1 Scheduling Fixed-head Devices
Fixed head disk = DRUM. One head per track on the drum.
Seek time = 0.
Latency time < moving head disk.
Figure 7.5: Scheduling Fixed-head Devices
Different algorithm is required for this device.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 243