Page 172 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 172
Unit 8: Database System
Notes
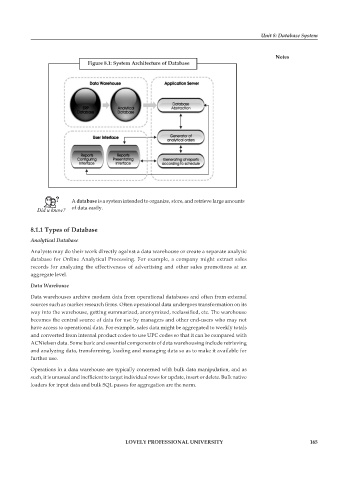
Figure 8.1: System Architecture of Database
A database is a system intended to organize, store, and retrieve large amounts
of data easily.
8.1.1 Types of Database
Analytical Database
Analysts may do their work directly against a data warehouse or create a separate analytic
database for Online Analytical Processing. For example, a company might extract sales
records for analyzing the effectiveness of advertising and other sales promotions at an
aggregate level.
Data Warehouse
Data warehouses archive modern data from operational databases and often from external
sources such as market research firms. Often operational data undergoes transformation on its
way into the warehouse, getting summarized, anonymized, reclassified, etc. The warehouse
becomes the central source of data for use by managers and other end-users who may not
have access to operational data. For example, sales data might be aggregated to weekly totals
and converted from internal product codes to use UPC codes so that it can be compared with
ACNielsen data. Some basic and essential components of data warehousing include retrieving
and analyzing data, transforming, loading and managing data so as to make it available for
further use.
Operations in a data warehouse are typically concerned with bulk data manipulation, and as
such, it is unusual and inefficient to target individual rows for update, insert or delete. Bulk native
loaders for input data and bulk SQL passes for aggregation are the norm.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 165