Page 175 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 175
Exposure to Computer Disciplines
Notes 8.1.2.2 Post-relational Database Models
Products offering a more general data model than the relational model are sometimes classified
as post-relational. Alternate terms include “hybrid database”, “Object-enhanced RDBMS” and
others. The data model in such products incorporates relations but is not constrained by E.F.
Codd’s Information Principle, which requires that all information in the database must be cast
explicitly in terms of values in relations and in no other way.
Some of these extensions to the relational model integrate concepts from technologies that pre-
date the relational model. For example, they allow representation of a directed graph with trees
on the nodes.
Some post-relational products extend relational systems with non-relational features. Others
arrived in much the same place by adding relational features to pre-relational systems.
Paradoxically, this allows products that are historically pre-relational, such as PICK and MUMPS,
to make a plausible claim to be post-relational.
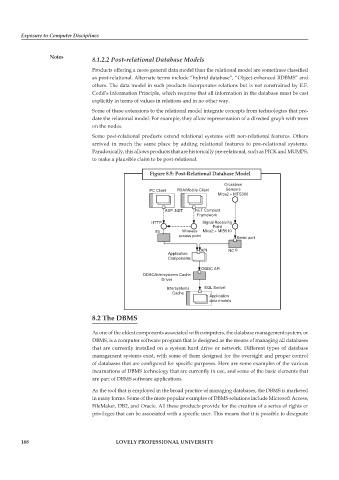
Figure 8.5: Post-Relational Database Model
Crossbow
PC Client PDA/Mobile Client Sensors
Mica2 + MTS300
ASP .NET .NET Compact
Framework
HTTP Signal Receiving
Point
IIS Wireless Mica2 + MIB510
access point Serial port
API NC
Application
Components
ODBC API
ODBC/Intersystems Cache
Driver
Intersystems SQL Socket
Cache
Application
data models
8.2 The DBMS
As one of the oldest components associated with computers, the database management system, or
DBMS, is a computer software program that is designed as the means of managing all databases
that are currently installed on a system hard drive or network. Different types of database
management systems exist, with some of them designed for the oversight and proper control
of databases that are configured for specific purposes. Here are some examples of the various
incarnations of DBMS technology that are currently in use, and some of the basic elements that
are part of DBMS software applications.
As the tool that is employed in the broad practice of managing databases, the DBMS is marketed
in many forms. Some of the more popular examples of DBMS solutions include Microsoft Access,
FileMaker, DB2, and Oracle. All these products provide for the creation of a series of rights or
privileges that can be associated with a specific user. This means that it is possible to designate
168 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY