Page 18 - DCAP105_WORKSHOP_ON_COMPUTER_HARDWARE_AND_NETWORK
P. 18
Workshop on Computer Hardware and Network
Notes machines had faded by the time we entered the New Millennium. The latest dye-sub
printers allegedly produce more archival prints but this whole technology seems to be
fading in favor of ink jet. Color management is a problem with dye-sub, as with ink jet.
These are CMYK devices.
Fujix 3000 (and now 4000): Though rather long in the tooth, this is the choice of most
imaging professionals. The Fujix machines uses three lasers to expose a specially treated
“donor paper” which is then thermally developed and transferred onto “receiver paper”.
It is a traditional silver halide process but one need not maintain chemistry or clean
processor rollers. Resolution is 400 dpi on an 8.5x11 sheet (Fujix 3500) or 12x18 (Fujix 4000).
Image quality is the best of any printer available, comparable to an Ilfochrome, and
archival qualities are reputed to be good. The printer is a standard piece of office equipment
and the expended donor paper goes back UPS to Fuji for recycling and disposal.
Consumables cost $2-4 per page and you can make transparencies as well as opaque
photos.
Barcode printers: Barcode printers typically come in fixed sizes of 4 inches, 6 inches or 8
inches wide. Although a number of manufacturers have made differing sizes in the past,
most have now standardised on these sizes. The main application for these printers is to
produce barcode labels for product and shipping identification.
Label Printers: Labels come in two main types: Thermal (sometimes referred to as Direct
Thermal) and Thermal Transfer. A huge variety of specialist materials and adhesives are
available to suit most applications. These include plain white paper packaging labels,
durable rating plates, and tamper-evident labels.
1.1.4 Storage Devices
Primary memory (especially RAM) stores the data, instructions and information temporarily
during processing by CPU. When the computer is switched off, this memory gets erased. How
does a computer store the data, information and software permanently, so that they can be
retrieved whenever required? Certainly, there must be some storage devices in the computer.
Now, we will discuss about different Storage Devices, sometimes also called as Secondary
Memory Devices.
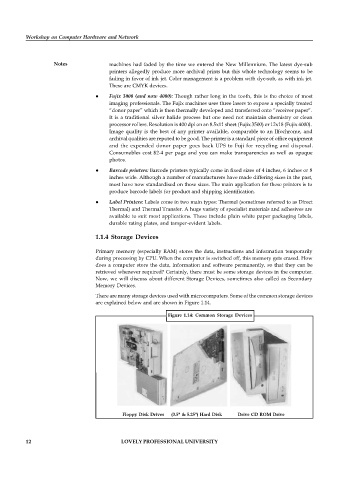
There are many storage devices used with microcomputers. Some of the common storage devices
are explained below and are shown in Figure 1.14.
Figure 1.14: Common Storage Devices
Floppy Disk Drives (3.5" & 5.25") Hard Disk Drive CD ROM Drive
12 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY