Page 215 - DCAP109_GRAPHIC_TOOLS
P. 215
Graphic Tools
Notes
Example: “http:// www.google.com”
There are fixed characters and numbers allowed in an URL.
z Unreserved
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 - _ . ~
z Reserved
! * ‘ ( ) ; : @ & = + $ , / ? % # [ ]
A URL consists of three parts:
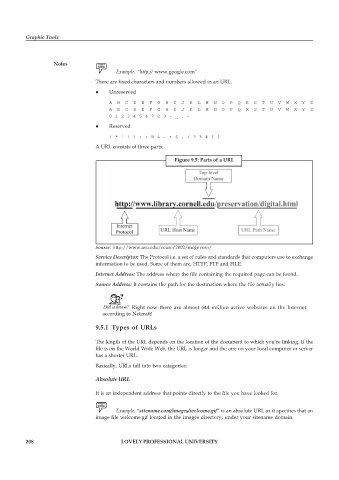
Figure 9.5: Parts of a URL
Source: http://www.asu.edu/ecure/2002/mcgovern/
Service Descriptor: The Protocol i.e. a set of rules and standards that computers use to exchange
information to be used. Some of them are, HTTP, FTP and FILE.
Internet Address: The address where the file containing the required page can be found.
Source Address: It contains the path for the destination where the file actually lies.
Did u know? Right now there are almost 644 million active websites on the Internet
according to Netcraft!
9.5.1 Types of URLs
The length of the URL depends on the location of the document to which you’re linking. If the
file is on the World Wide Web, the URL is longer and the one on your local computer or server
has a shorter URL.
Basically, URLs fall into two categories:
Absolute URL
It is an independent address that points directly to the file you have looked for.
Example: “sitename.com/images/welcome.gif” is an absolute URL as it specifies that an
image file welcome.gif located in the images directory, under your sitename domain.
208 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY