Page 140 - DCAP208_Management Support Systems
P. 140
Unit 9: Data Mining
memos in textual forms often exchanged by e-mail. These messages are regularly stored Notes
in digital form for future use and reference creating formidable digital libraries.
The World Wide Web repositories: Since the inception of the World Wide Web in 1993,
documents of all sorts of formats, content and description have been collected and inter-
connected with hyperlinks making it the largest repository of data ever built. Despite its
dynamic and unstructured nature, its heterogeneous characteristic, and its very often
redundancy and inconsistency, the World Wide Web is the most important data collection
regularly used for reference because of the broad variety of topics covered and the infinite
contributions of resources and publishers. Many believe that the World Wide Web will
become the compilation of human knowledge.
9.1.2 Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery
With the enormous amount of data stored in files, databases, and other repositories, it is
increasingly important, if not necessary, to develop powerful means for analysis and perhaps
interpretation of such data and for the extraction of interesting knowledge that could help in
decision-making.
Data Mining, also popularly known as Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD), refers to the
nontrivial extraction of implicit, previously unknown and potentially useful information from
data in databases.
Did u know? While data mining and knowledge discovery in databases (or KDD) are
frequently treated as synonyms, data mining is actually part of the knowledge discovery
process.
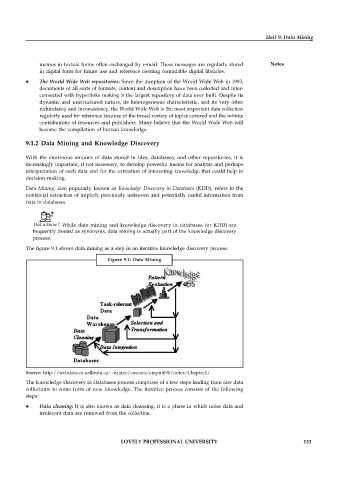
The figure 9.1 shows data mining as a step in an iterative knowledge discovery process.
Figure 9.1: Data Mining
Source: http://webdocs.cs.ualberta.ca/~zaiane/courses/cmput690/notes/Chapter1/
The Knowledge Discovery in Databases process comprises of a few steps leading from raw data
collections to some form of new knowledge. The iterative process consists of the following
steps:
Data cleaning: It is also known as data cleansing, it is a phase in which noise data and
irrelevant data are removed from the collection.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 133