Page 87 - DCAP208_Management Support Systems
P. 87
Management Support Systems
Notes 3. Data warehouse layer: Information is stored to one logically centralized single repository:
a data warehouse. The data warehouse can be directly accessed, but it can also be used as
a source for creating data marts, which partially replicate data warehouse contents and are
designed for specific enterprise departments. Metadata repositories store information on
sources, access procedures, data staging, users, data mart schemata, and so on.
4. Analysis: In this layer, integrated data is efficiently and flexibly accessed to issue reports,
dynamically analyze information, and simulate hypothetical business scenarios.
Technologically speaking, it should feature aggregate data navigators, complex query
optimizers, and user-friendly GUIs.
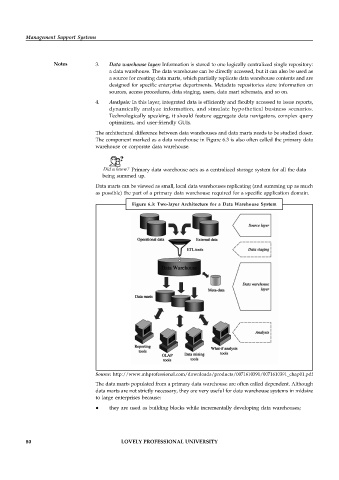
The architectural difference between data warehouses and data marts needs to be studied closer.
The component marked as a data warehouse in Figure 6.3 is also often called the primary data
warehouse or corporate data warehouse.
Did u know? Primary data warehouse acts as a centralized storage system for all the data
being summed up.
Data marts can be viewed as small, local data warehouses replicating (and summing up as much
as possible) the part of a primary data warehouse required for a specific application domain.
Figure 6.3: Two-layer Architecture for a Data Warehouse System
Source: http://www.mhprofessional.com/downloads/products/0071610391/0071610391_chap01.pdf
The data marts populated from a primary data warehouse are often called dependent. Although
data marts are not strictly necessary, they are very useful for data warehouse systems in midsize
to large enterprises because:
they are used as building blocks while incrementally developing data warehouses;
80 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY