Page 90 - DCAP208_Management Support Systems
P. 90
Unit 6: Data Warehousing
The bus architecture, recommended by Ralph Kimball, is apparently similar to the preceding Notes
architecture, with one important difference. A basic set of conformed dimensions (that is, analysis
dimensions that preserve the same meaning throughout all the facts they belong to), derived by
a careful analysis of the main enterprise processes, is adopted and shared as a common design
guideline. This ensures logical integration of data marts and an enterprise-wide view of
information.
In the hub and spoke architecture, one of the most used in medium to large contexts, there is
much attention to scalability and extensibility, and to achieving an enterprise-wide view of
information. Atomic, normalized data is stored in a reconciled layer that feeds a set of data
marts containing summarized data in multidimensional form (Figure 6.6). Users mainly access
the data marts, but they may occasionally query the reconciled layer.
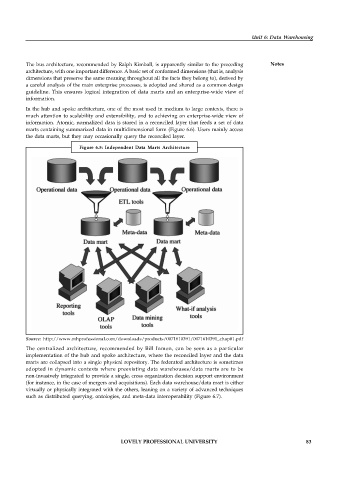
Figure 6.5: Independent Data Marts Architecture
Source: http://www.mhprofessional.com/downloads/products/0071610391/0071610391_chap01.pdf
The centralized architecture, recommended by Bill Inmon, can be seen as a particular
implementation of the hub and spoke architecture, where the reconciled layer and the data
marts are collapsed into a single physical repository. The federated architecture is sometimes
adopted in dynamic contexts where preexisting data warehouses/data marts are to be
non-invasively integrated to provide a single, cross organization decision support environment
(for instance, in the case of mergers and acquisitions). Each data warehouse/data mart is either
virtually or physically integrated with the others, leaning on a variety of advanced techniques
such as distributed querying, ontologies, and meta-data interoperability (Figure 6.7).
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 83