Page 89 - DCAP305_PRINCIPLES_OF_SOFTWARE_ENGINEERING
P. 89
Unit 4: Introduction to Validation, Metrics
• Scalability: Because tiers are based on the deployment of layers, scaling out an application Notes
is reasonably straightforward.
• Flexibility: Because each tier can be managed or scaled independently, flexibility is
increased.
• Availability: Applications can exploit the modular architecture of enabling systems using
easily scalable components, which increases availability.
Consider either the N-tier or the 3-tier architectural style if the processing requirements of
the layers in the application differ such that processing in one layer could absorb sufficient
resources to slow the processing in other layers, or if the security requirements of the layers in
the application differ. For example, the presentation layer should not store sensitive data, while
this may be stored in the business and data layers. The N-tier or the 3-tier architectural style is
also appropriate if you want to be able to share business logic between applications, and you
have sufficient hardware to allocate the required number of servers to each tier.
Consider using just three tiers if you are developing an intranet application where all servers
are located within the private network; or an Internet application where security requirements
do not restrict the deployment of business logic on the public facing Web or application server.
Consider using more than three tiers if security requirements dictate that business logic cannot
be deployed to the perimeter network, or the application makes heavy use of resources and you
want to offload that functionality to another server
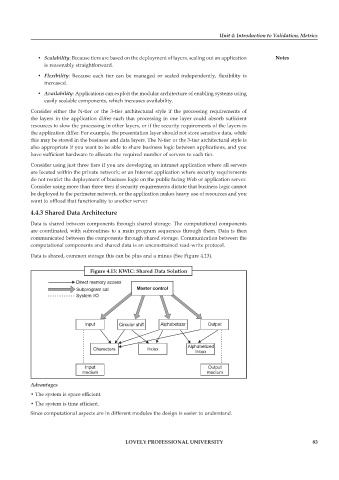
4.4.3 Shared Data Architecture
Data is shared between components through shared storage. The computational components
are coordinated, with subroutines to a main program sequences through them. Data is then
communicated between the components through shared storage. Communication between the
computational components and shared data is an unconstrained read-write protocol.
Data is shared, common storage this can be plus and a minus (See Figure 4.13).
Figure 4.13: KWIC: Shared Data Solution
Advantages
• The system is space efficient.
• The system is time efficient.
Since computational aspects are in different modules the design is easier to understand.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 83