Page 189 - DCAP312_WEB_TECHNOLOGIES_II
P. 189
Unit 9: The Database Model
Rule 2: Every object is instance of a class. Notes
Rule 3: A class defines the behavior via public methods and the structure of its instances via
instance variables which are private to the instances.
Rule 4: Each class is inheriting its behavior and structure description from a single superclass.
Rule 5: Objects only communicate via message passing (i.e., method invocation). When an object
receives a message, the corresponding method is looked up in the class of the receiver,
then if not found on this class continues in the class’s superclasses.
Rule 6: The class Object is the root of the inheritance tree (in Squeak this is ProtoObject the class
that represents objects understanding the smallest set of messages).
Rule 7: Classes are instances too. They are instances of other classes called metaclasses.
9.6.1 Model Precisions
In Smalltalk we have only objects that are instance of classes. Class defines the structure of the
instance in terms of instance variables, and methods.
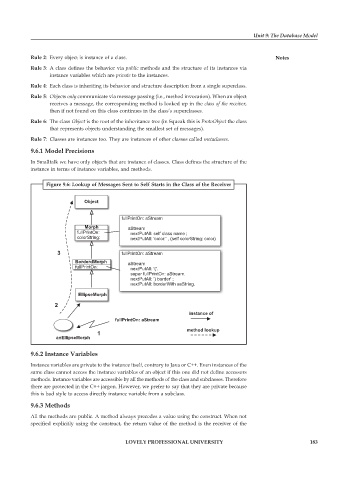
Figure 9.6: Lookup of Messages Sent to Self Starts in the Class of the Receiver
Object
fullPrintOn: aStream
Morph aStream
fullPrintOn: nextPutAll: self class name ;
colorString: nextPutAll: 'color:' , (self colorString: color)
3 fullPrintOn: aStream
BorderdMorph aStream
fullPrintOn: nextPutAll: '('.
super fullPrintOn: aStream.
nextPutAll: ') border' ;
nextPutAll: borderWith asString.
EllipseMorph
2
instance of
fullPrintOn: aStream
method lookup
1
anEllipseMorph
9.6.2 Instance Variables
Instance variables are private to the instance itself, contrary to Java or C++. Even instances of the
same class cannot access the instance variables of an object if this one did not define accessors
methods. Instance variables are accessible by all the methods of the class and subclasses. Therefore
there are protected in the C++ jargon. However, we prefer to say that they are private because
this is bad style to access directly instance variable from a subclass.
9.6.3 Methods
All the methods are public. A method always precedes a value using the construct. When not
specified explicitly using the construct, the return value of the method is the receiver of the
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 183