Page 193 - DCAP312_WEB_TECHNOLOGIES_II
P. 193
Unit 9: The Database Model
piece of the puzzle affects the entire picture. Use cases interoperations and interactions Notes
are to be determined and the information flow for each case is specified.
• Form Detail Determination
This stage includes declaring the form details. This high level definition will help us not
only to decrease our dependency to different platforms but also to make it possible for
high level users to design a form, so that they could describe their forms in an abstract
form. There are some well known innovated tools/standards that are suitable for this
methodology such as XForms standard. It will bring a distinct part in conjugation with
XML standards to design a form. Another example is XUL. Generally our output can be
one of the HTML, XForms, XUL, MS Word, or Pdf formats.
• Interface Functional Definition
In this totally conceptual stage, an interface is defined by defining its functionality. This
is done by answering a series of questions as shown below:
○ What kind or type of information does the form get?
○ What kind of necessary constraints does a particular field in the form have?
○ How do the form objects relate to the information other forms? (For example contents/
items in the combo boxes, option lists, …)
In this part another important aspect of XForms is discovered. This, in conjugations with other
XML standards, provides capabilities to declare the form model absolutely independent of the
logic behind the interface.
Analysis and Object Production Phase
The output of the previous phase is an XForms document, which includes the design and
logic of the form. All the designed items are coming from a standard template. The XForm
document maintains the design and the logic of the form as a standard relation between
Design and Development phase. This is the main phase in our proposed method. It receives the
structured input in the special format of XForm, and transforms it to a well-defined format of the
programming languages. In fact this part will parse text into objects as declared. This part will
generate the data model as a data structure, considering the input fields of the form. Also, proper
communication means to other classes and objects are considered in the class definition. The
methods are defined in a very abstract and general form since the classes are made dynamically.
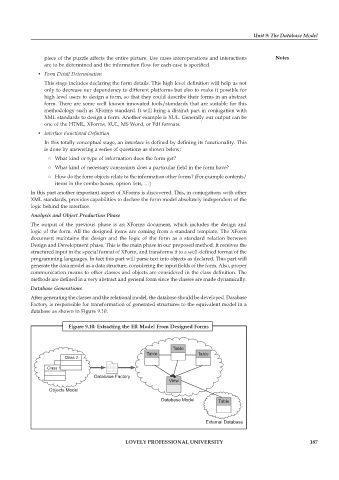
Database Generations
After generating the classes and the relational model, the database should be developed. Database
Factory is responsible for transformation of generated structures to the equivalent model in a
database as shown in Figure 9.10.
Figure 9.10: Extracting the ER Model From Designed Forms
Table
Table Table
Class 2
Class 1
Database Factory
View
Objects Model
Database Model Table
External Database
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 187