Page 194 - DCAP403_Operating System
P. 194
Unit 10: System Protection
Notes
g g
A B A B
w w
w
A Grants (w to D) to B
D D
Grant
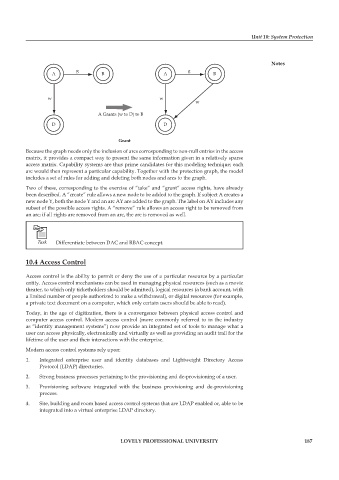
Because the graph needs only the inclusion of arcs corresponding to non-null entries in the access
matrix, it provides a compact way to present the same information given in a relatively sparse
access matrix. Capability systems are thus prime candidates for this modeling technique; each
arc would then represent a particular capability. Together with the protection graph, the model
includes a set of rules for adding and deleting both nodes and arcs to the graph.
Two of these, corresponding to the exercise of “take” and “grant” access rights, have already
been described. A “create” rule allows a new node to be added to the graph. If subject A creates a
new node Y, both the node Y and an arc AY are added to the graph. The label on AY includes any
subset of the possible access rights. A “remove” rule allows an access right to be removed from
an arc; if all rights are removed from an arc, the arc is removed as well.
Task Differentiate between DAC and RBAC concept.
10.4 Access Control
Access control is the ability to permit or deny the use of a particular resource by a particular
entity. Access control mechanisms can be used in managing physical resources (such as a movie
theater, to which only ticketholders should be admitted), logical resources (a bank account, with
a limited number of people authorized to make a withdrawal), or digital resources (for example,
a private text document on a computer, which only certain users should be able to read).
Today, in the age of digitization, there is a convergence between physical access control and
computer access control. Modern access control (more commonly referred to in the industry
as “identity management systems”) now provide an integrated set of tools to manage what a
user can access physically, electronically and virtually as well as providing an audit trail for the
lifetime of the user and their interactions with the enterprise.
Modern access control systems rely upon:
1. Integrated enterprise user and identity databases and Lightweight Directory Access
Protocol (LDAP) directories.
2. Strong business processes pertaining to the provisioning and de-provisioning of a user.
3. Provisioning software integrated with the business provisioning and de-provisioning
process.
4. Site, building and room based access control systems that are LDAP enabled or, able to be
integrated into a virtual enterprise LDAP directory.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 187