Page 188 - DMGT409Basic Financial Management
P. 188
Unit 11: Cash Management
Notes
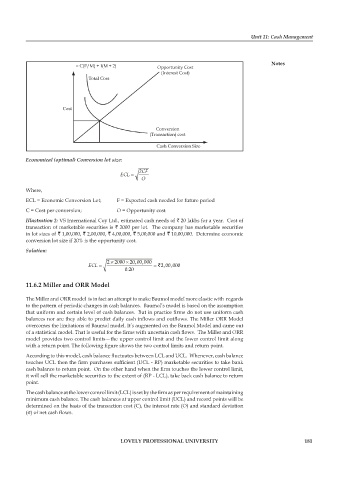
= C(F/M) + I(M ÷ 2) Opportunity Cost
(Interest Cost)
Total Cost
Cost
Conversion
(Transaction) cost
Cash Conversion Size
Economical (optimal) Conversion lot size:
2CF
ECL =
O
Where,
ECL = Economic Conversion Lot; F = Expected cash needed for future period
C = Cost per conversion; O = Opportunity cost
Illustration 2: VS International Coy Ltd., estimated cash needs of ` 20 lakhs for a year. Cost of
transaction of marketable securities is ` 2000 per lot. The company has marketable securities
in lot sizes of ` 1,00,000, ` 2,00,000, ` 4,00,000, ` 5,00,000 and ` 10,00,000. Determine economic
conversion lot size if 20% is the opportunity cost.
Solution:
×
×
2 2000 20,00,000
ECL = = ` 2,00,000
0.20
11.6.2 Miller and ORR Model
The Miller and ORR model is in fact an attempt to make Baumol model more elastic with regards
to the pattern of periodic changes in cash balances. Baumol’s model is based on the assumption
that uniform and certain level of cash balances. But in practice firms do not use uniform cash
balances nor are they able to predict daily cash inflows and outflows. The Miller ORR Model
overcomes the limitations of Baumol model. It’s augmented on the Baumol Model and came out
of a statistical model. That is useful for the firms with uncertain cash flows. The Miller and ORR
model provides two control limits—the upper control limit and the lower control limit along
with a return point. The following figure shows the two control limits and return point.
According to this model, cash balance fluctuates between LCL and UCL. Whenever, cash balance
touches UCL then the firm purchases sufficient (UCL - RP) marketable securities to take bank
cash balance to return point. On the other hand when the firm touches the lower control limit,
it will sell the marketable securities to the extent of (RP - LCL), take back cash balance to return
point.
The cash balance at the lower control limit (LCL) is set by the firm as per requirement of maintaining
minimum cash balance. The cash balances at upper control limit (UCL) and record points will be
determined on the basis of the transaction cost (C), the interest rate (O) and standard deviation
(σ) of net cash fl ows.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 181