Page 191 - DMGT409Basic Financial Management
P. 191
Basic Financial Management
Notes
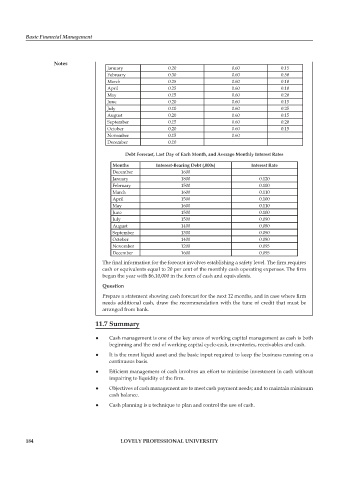
January 0.20 0.60 0.15
February 0.30 0.60 0.50
March 0.25 0.60 0.10
April 0.25 0.60 0.10
May 0.15 0.60 0.20
June 0.20 0.60 0.15
July 0.10 0.60 0.25
August 0.20 0.60 0.15
September 0.15 0.60 0.20
October 0.20 0.60 0.15
November 0.15 0.60
December 0.10
Debt Forecast, Last Day of Each Month, and Average Monthly Interest Rates
Months Interest-Bearing Debt (,000s) Interest Rate
December 1600
January 1800 0.120
February 1500 0.100
March 1600 0.110
April 1500 0.100
May 1600 0.110
June 1500 0.100
July 1500 0.090
August 1400 0.080
September 1300 0.090
October 1400 0.080
November 1200 0.095
December 1600 0.095
The final information for the forecast involves establishing a safety level. The fi rm requires
cash or equivalents equal to 20 per cent of the monthly cash operating expenses. The fi rm
began the year with $6,10,000 in the form of cash and equivalents.
Question
Prepare a statement showing cash forecast for the next 12 months, and in case where fi rm
needs additional cash, draw the recommendation with the tune of credit that must be
arranged from bank.
11.7 Summary
Cash management is one of the key areas of working capital management as cash is both
beginning and the end of working capital cycle-cash, inventories, receivables and cash.
It is the most liquid asset and the basic input required to keep the business running on a
continuous basis.
Efficient management of cash involves an effort to minimise investment in cash without
impairing to liquidity of the fi rm.
Objectives of cash management are to meet cash payment needs; and to maintain minimum
cash balance.
Cash planning is a technique to plan and control the use of cash.
184 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY