Page 88 - DMGT409Basic Financial Management
P. 88
Unit 5: Capital Structure Decisions
2. Second: Variable costs that varies directly with the level of production. Notes
Example: Raw materials, direct labour costs, etc.
3. Third: Semi-variable costs, which partly vary and is partly fi xed.
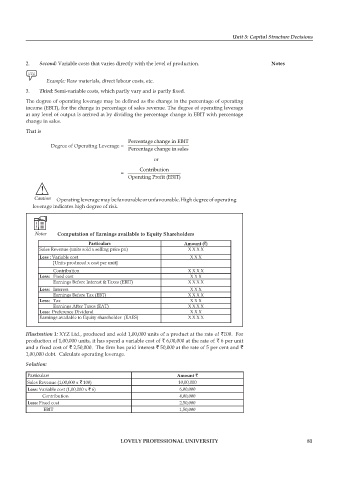
The degree of operating leverage may be defined as the change in the percentage of operating
income (EBIT), for the change in percentage of sales revenue. The degree of operating leverage
at any level of output is arrived at by dividing the percentage change in EBIT with percentage
change in sales.
That is
Percentage change in EBIT
Degree of Operating Leverage =
Percentage change in sales
or
Contribution
=
Operating Profit (EBIT)
!
Caution Operating leverage may be favourable or unfavourable. High degree of operating
leverage indicates high degree of risk.
Notes Computation of Earnings available to Equity Shareholders
Particulars Amount (`)
Sales Revenue (units sold x selling price pu) X X X X
Less : Variable cost X X X
[Units produced x cost per unit]
Contribution X X X X
Less: Fixed cost X X X
Earnings Before Interest & Taxes (EBIT) X X X X
Less: Interest X X X
Earnings Before Tax (EBT) X X X X
Less: Tax X X X
Earnings After Taxes (EAT) X X X X
Less: Preference Dividend X X X
Earnings available to Equity shareholder (EAES) X X X X
Illustration 1: XYZ Ltd., produced and sold 1,00,000 units of a product at the rate of `100. For
production of 1,00,000 units, it has spend a variable cost of ` 6,00,000 at the rate of ` 6 per unit
and a fixed cost of ` 2,50,000. The firm has paid interest ` 50,000 at the rate of 5 per cent and `
1,00,000 debt. Calculate operating leverage.
Solution:
Particulars Amount `
Sales Revenue (1,00,000 x ` 100) 10,00,000
Less: Variable cost (1,00,000 x ` 6) 6,00,000
Contribution 4,00,000
Less: Fixed cost 2,50,000
EBIT 1,50,000
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 81