Page 168 - SOFTWARE TESTING & QUALITY ASSURANCE
P. 168
Unit 11: Test Case Planning
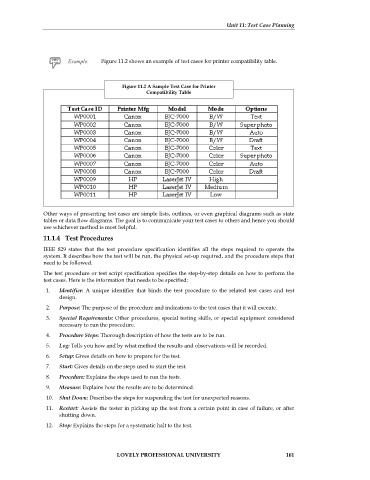
Figure 11.2 shows an example of test cases for printer compatibility table.
Figure 11.2 A Sample Test Case for Printer
Compatibility Table
Other ways of presenting test cases are simple lists, outlines, or even graphical diagrams such as state
tables or data flow diagrams. The goal is to communicate your test cases to others and hence you should
use whichever method is most helpful.
11.1.4 Test Procedures
IEEE 829 states that the test procedure specification identifies all the steps required to operate the
system. It describes how the test will be run, the physical set-up required, and the procedure steps that
need to be followed.
The test procedure or test script specification specifies the step-by-step details on how to perform the
test cases. Here is the information that needs to be specified:
1. Identifier: A unique identifier that binds the test procedure to the related test cases and test
design.
2. Purpose: The purpose of the procedure and indications to the test cases that it will execute.
3. Special Requirements: Other procedures, special testing skills, or special equipment considered
necessary to run the procedure.
4. Procedure Steps: Thorough description of how the tests are to be run.
5. Log: Tells you how and by what method the results and observations will be recorded.
6. Setup: Gives details on how to prepare for the test.
7. Start: Gives details on the steps used to start the test.
8. Procedure: Explains the steps used to run the tests.
9. Measure: Explains how the results are to be determined.
10. Shut Down: Describes the steps for suspending the test for unexpected reasons.
11. Restart: Assists the tester in picking up the test from a certain point in case of failure, or after
shutting down.
12. Stop: Explains the steps for a systematic halt to the test.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 161