Page 36 - DCAP504_Computer Graphics
P. 36
Unit 3: Overview of Graphics I/O Devices
second, or Hertz (Hz), where a cycle corresponds to one frame. Using these units, a refresh rate of 60
frames per second is described as 60 Hz. The electron beam returns to the left side of the screen to begin
displaying the next scan line. The return to the left of the screen, after refreshing each scan line, is called
the horizontal retrace of the electron beam. At the end of each frame, the electron beam returns to the
top left corner of the screen to begin the next frame.
On some raster-scan systems (and in TV sets), each frame is displayed in two passes using an interlaced
refresh procedure. In the first pass, the beam sweeps across every other scan line from top to bottom.
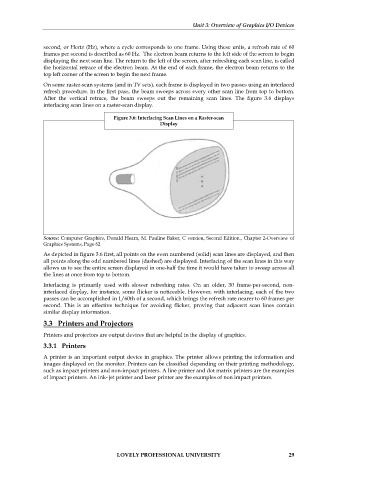
After the vertical retrace, the beam sweeps out the remaining scan lines. The figure 3.6 displays
interlacing scan lines on a raster-scan display.
Figure 3.6: Interlacing Scan Lines on a Raster-scan
Display
Source: Computer Graphics, Donald Hearn, M. Pauline Baker, C version, Second Edition., Chapter 2-Overview of
Graphics Systems, Page 62
As depicted in figure 3.6 first, all points on the even numbered (solid) scan lines are displayed, and then
all points along the odd numbered lines (dashed) are displayed. Interlacing of the scan lines in this way
allows us to see the entire screen displayed in one-half the time it would have taken to sweep across all
the lines at once from top to bottom.
Interlacing is primarily used with slower refreshing rates. On an older, 30 frame-per-second, non-
interlaced display, for instance, some flicker is noticeable. However, with interlacing, each of the two
passes can be accomplished in 1/60th of a second, which brings the refresh rate nearer to 60 frames per
second. This is an effective technique for avoiding flicker, proving that adjacent scan lines contain
similar display information.
3.3 Printers and Projectors
Printers and projectors are output devices that are helpful in the display of graphics.
3.3.1 Printers
A printer is an important output device in graphics. The printer allows printing the information and
images displayed on the monitor. Printers can be classified depending on their printing methodology,
such as impact printers and non-impact printers. A line printer and dot matrix printers are the examples
of impact printers. An ink- jet printer and laser printer are the examples of non impact printers.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 29