Page 55 - DCAP504_Computer Graphics
P. 55
Computer Graphics
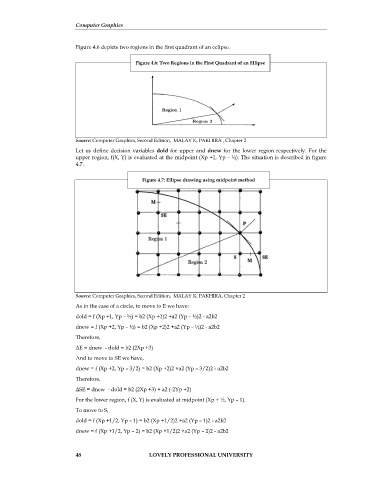
Figure 4.6 depicts two regions in the first quadrant of an eclipse.
Figure 4.6: Two Regions in the First Quadrant of an Ellipse
Source: Computer Graphics, Second Edition, MALAY K, PAKHIRA , Chapter 2
Let us define decision variables dold for upper and dnew for the lower region respectively. For the
upper region, f(X, Y) is evaluated at the midpoint (Xp +1, Yp – ½). The situation is described in figure
4.7.
Figure 4.7: Ellipse drawing using midpoint method
Source: Computer Graphics, Second Edition, MALAY K, PAKHIRA, Chapter 2
As in the case of a circle, to move to E we have:
dold = f (Xp +1, Yp – ½) = b2 (Xp +1)2 +a2 (Yp – ½)2 - a2b2
dnew = f (Xp +2, Yp – ½) = b2 (Xp +2)2 +a2 (Yp – ½)2 - a2b2
Therefore,
ΔE = dnew - dold = b2 (2Xp +3)
And to move to SE we have,
dnew = f (Xp +2, Yp – 3/2) = b2 (Xp +2)2 +a2 (Yp – 3/2)2 - a2b2
Therefore,
ΔSE = dnew - dold = b2 (2Xp +3) + a2 (-2Yp +2)
For the lower region, f (X, Y) is evaluated at midpoint (Xp + ½, Yp – 1).
To move to S,
dold = f (Xp +1/2, Yp – 1) = b2 (Xp +1/2)2 +a2 (Yp – 1)2 - a2b2
dnew = f (Xp +1/2, Yp – 2) = b2 (Xp +1/2)2 +a2 (Yp – 2)2 - a2b2
48 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY