Page 62 - DCAP504_Computer Graphics
P. 62
Unit 5: Scan Conversion II
Two important properties are required to scan convert polygons:
1. Spatial Coherence: This property states that the adjacent pixels of the polygons usually have the
same characteristics.
2. Scan Line Coherence: This property states that scan line will have the same characteristics.
Many algorithms are used to scan convert a polygon. Parity scan conversion algorithm is one of the
most popular algorithms. This algorithm is based on parity bit. Figure 5.2 (a) illustrates the parity scan
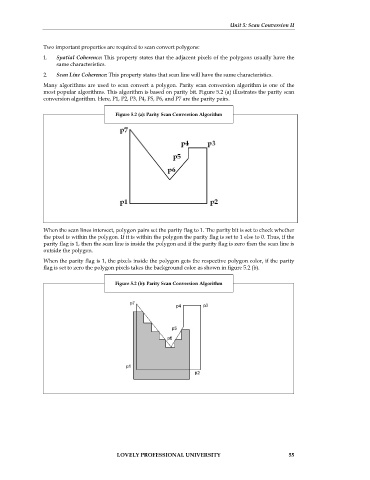
conversion algorithm. Here, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, and P7 are the parity pairs.
Figure 5.2 (a): Parity Scan Conversion Algorithm
When the scan lines intersect, polygon pairs set the parity flag to 1. The parity bit is set to check whether
the pixel is within the polygon. If it is within the polygon the parity flag is set to 1 else to 0. Thus, if the
parity flag is 1, then the scan line is inside the polygon and if the parity flag is zero then the scan line is
outside the polygon.
When the parity flag is 1, the pixels inside the polygon gets the respective polygon color, if the parity
flag is set to zero the polygon pixels takes the background color as shown in figure 5.2 (b).
Figure 5.2 (b): Parity Scan Conversion Algorithm
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 55