Page 11 - DCAP603_DATAWARE_HOUSING_AND_DATAMINING
P. 11
Unit 1: Data Warehouse Practice
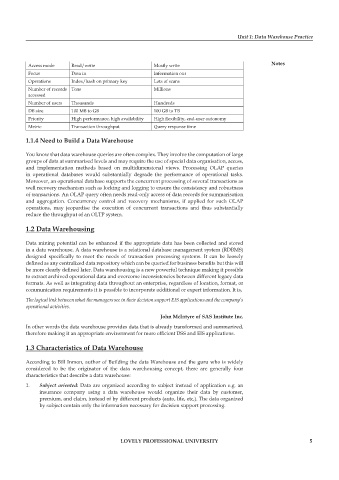
Access mode Read/write Mostly write notes
Focus Data in Information out
Operations Index/hash on primary key Lots of scans
Number of records Tens Millions
accessed
Number of users Thousands Hundreds
DB size 100 MB to GB 100 GB to TB
Priority High performance, high availability High flexibility, end-user autonomy
Metric Transaction throughput Query response time
1.1.4 need to Build a Data Warehouse
You know that data warehouse queries are often complex. They involve the computation of large
groups of data at summarised levels and may require the use of special data organisation, access,
and implementation methods based on multidimensional views. Processing OLAP queries
in operational databases would substantially degrade the performance of operational tasks.
Moreover, an operational database supports the concurrent processing of several transactions as
well recovery mechanism such as locking and logging to ensure the consistency and robustness
of transactions. An OLAP query often needs read-only access of data records for summarisation
and aggregation. Concurrency control and recovery mechanisms, if applied for such OLAP
operations, may jeopardise the execution of concurrent transactions and thus substantially
reduce the throughput of an OLTP system.
1.2 Data Warehousing
Data mining potential can be enhanced if the appropriate data has been collected and stored
in a data warehouse. A data warehouse is a relational database management system (RDBMS)
designed specifically to meet the needs of transaction processing systems. It can be loosely
defined as any centralized data repository which can be queried for business benefits but this will
be more clearly defined later. Data warehousing is a new powerful technique making it possible
to extract archived operational data and overcome inconsistencies between different legacy data
formats. As well as integrating data throughout an enterprise, regardless of location, format, or
communication requirements it is possible to incorporate additional or expert information. It is,
The logical link between what the managers see in their decision support EIS applications and the company’s
operational activities.
John Mcintyre of sas institute inc.
In other words the data warehouse provides data that is already transformed and summarized,
therefore making it an appropriate environment for more efficient DSS and EIS applications.
1.3 characteristics of Data Warehouse
According to Bill Inmon, author of Building the data Warehouse and the guru who is widely
considered to be the originator of the data warehousing concept, there are generally four
characteristics that describe a data warehouse:
1. Subject oriented: Data are organized according to subject instead of application e.g. an
insurance company using a data warehouse would organize their data by customer,
premium, and claim, instead of by different products (auto, life, etc,). The data organized
by subject contain only the information necessary for decision support processing.
LoveLy professionaL university 5