Page 12 - DCAP603_DATAWARE_HOUSING_AND_DATAMINING
P. 12
Data Warehousing and Data Mining
notes 2. Integrated: When data resides in many separate applications in the operational environment,
encoding of data is often inconsistent. For instance, in one application, gender might be
coded as “m” and “f” in another by 0 and 1. When data are moved from the operational
environment into the data warehouse, they assume a consistent coding convention e.g.
gender data is transformed to “m” and “f”.
3. Time variant: The data warehouse contains a place for storing data that are five to 10
years old, or older, to be used for comparisons, trends, and forecasting. These data are not
updated.
4. Non volatile: Data are not updated or changed in any way once they enter the data
warehouse, but are only loaded and accessed.
Task You know about store room and warehouse. Exactly what the difference
between warehouse and data warehouse? Explain with the suitable of suitable
example.
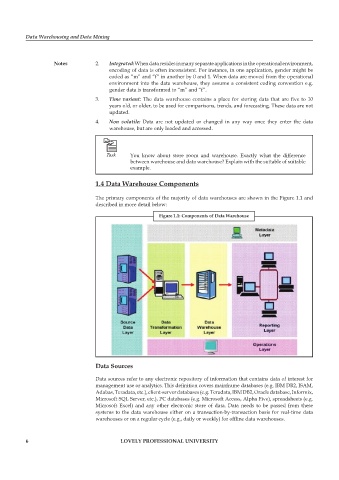
1.4 Data Warehouse components
The primary components of the majority of data warehouses are shown in the Figure 1.1 and
described in more detail below:
figure 1.1: components of Data Warehouse
Data sources
Data sources refer to any electronic repository of information that contains data of interest for
management use or analytics. This definition covers mainframe databases (e.g. IBM DB2, ISAM,
Adabas, Teradata, etc.), client-server databases (e.g. Teradata, IBM DB2, Oracle database, Informix,
Microsoft SQL Server, etc.), PC databases (e.g. Microsoft Access, Alpha Five), spreadsheets (e.g.
Microsoft Excel) and any other electronic store of data. Data needs to be passed from these
systems to the data warehouse either on a transaction-by-transaction basis for real-time data
warehouses or on a regular cycle (e.g., daily or weekly) for offline data warehouses.
6 LoveLy professionaL university