Page 17 - DCAP603_DATAWARE_HOUSING_AND_DATAMINING
P. 17
Unit 1: Data Warehouse Practice
refreshment, data source synchronisation, planning for disaster recovery, managing access control notes
and security, managing data growth, managing database performance, and data warehouse
enhancement and extension.
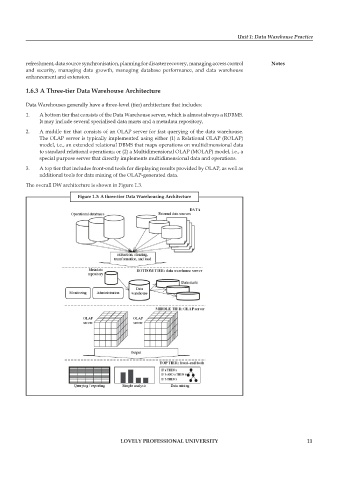
1.6.3 a three-tier Data Warehouse architecture
Data Warehouses generally have a three-level (tier) architecture that includes:
1. A bottom tier that consists of the Data Warehouse server, which is almost always a RDBMS.
It may include several specialised data marts and a metadata repository,
2. A middle tier that consists of an OLAP server for fast querying of the data warehouse.
The OLAP server is typically implemented using either (1) a Relational OLAP (ROLAP)
model, i.e., an extended relational DBMS that maps operations on multidimensional data
to standard relational operations; or (2) a Multidimensional OLAP (MOLAP) model, i.e., a
special purpose server that directly implements multidimensional data and operations.
3. A top tier that includes front-end tools for displaying results provided by OLAP, as well as
additional tools for data mining of the OLAP-generated data.
The overall DW architecture is shown in Figure 1.3.
figure 1.3: a three-tier Data Warehousing architecture
LoveLy professionaL university 11