Page 201 - DCAP603_DATAWARE_HOUSING_AND_DATAMINING
P. 201
Unit 10: Multi-dimensional Data Models and Aggregation
notes
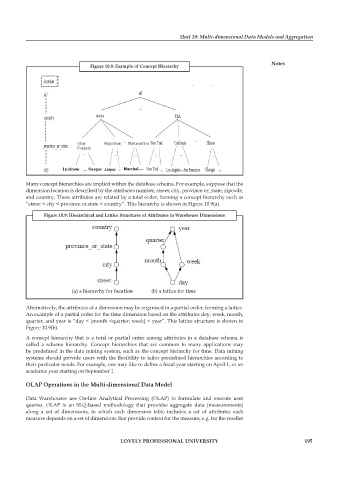
figure 10.8: example of concept hierarchy
Many concept hierarchies are implicit within the database schema. For example, suppose that the
dimension location is described by the attributes number, street, city, province-or_state, zipcode,
and country. These attributes are related by a total order, forming a concept hierarchy such as
“street < city < province.or.state < country”. This hierarchy is shown in Figure 10.9(a).
figure 10.9: hierarchical and Lattice structures of attributes in Warehouse Dimensions
(a) a hierarchy for location (b) a lattice for time
Alternatively, the attributes of a dimension may be organised in a partial order, forming a lattice.
An example of a partial order for the time dimension based on the attributes day, week, month,
quarter, and year is “day < {month <quarter; week} < year”. This lattice structure is shown in
Figure 10.9(b).
A concept hierarchy that is a total or partial order among attributes in a database schema is
called a schema hierarchy. Concept hierarchies that are common to many applications may
be predefined in the data mining system, such as the concept hierarchy for time. Data mining
systems should provide users with the flexibility to tailor predefined hierarchies according to
their particular needs. For example, one may like to define a fiscal year starting on April 1, or an
academic year starting on September 1.
oLap operations in the Multi-dimensional Data Model
Data Warehouses use On-line Analytical Processing (OLAP) to formulate and execute user
queries. OLAP is an SLQ-based methodology that provides aggregate data (measurements)
along a set of dimensions, in which each dimension table includes a set of attributes each
measure depends on a set of dimensions that provide context for the measure, e.g. for the reseller
LoveLy professionaL university 195