Page 127 - DCAP605_ADVANCED_DATA_STRUCTURE_AND_ALGORITHMS
P. 127
Advanced Data Structure and Algorithms
Notes boolean search(tnode *p, int val)
{
boolean ans;
tnode *temp;
temp = p;
ans = false;
while ((temp != NULL) && (!ans))
{
if(temp->data == val)
ans = true;
else
if(temp->data > val)
temp = temp->left;
else
temp = temp->right;
}
}
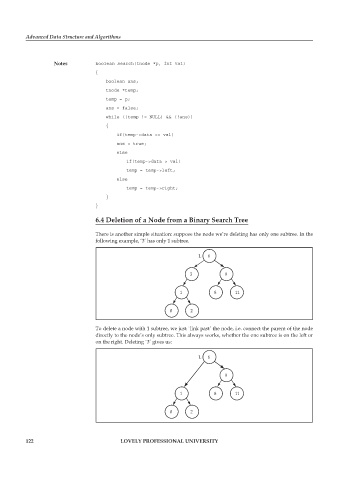
6.4 Deletion of a Node from a Binary Search Tree
There is another simple situation: suppose the node we’re deleting has only one subtree. In the
following example, ‘3’ has only 1 subtree.
L 6
3 9
1 8 11
0 2
To delete a node with 1 subtree, we just `link past’ the node, i.e. connect the parent of the node
directly to the node’s only subtree. This always works, whether the one subtree is on the left or
on the right. Deleting `3’ gives us:
L 6
9
1 8 11
0 2
122 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY