Page 15 - DCAP605_ADVANCED_DATA_STRUCTURE_AND_ALGORITHMS
P. 15
Advanced Data Structure and Algorithms
Notes Now, this size cannot be changed while running the program. This we all know is static allocation.
When writing the program, we have to decide on the maximum amount of memory that would
be needed. If we run the program on a small collection of data, then much of the space will
go waste. If program is run on bigger collection of data, then we may exhaust the space and
encounter an overflow. Consider the following example:
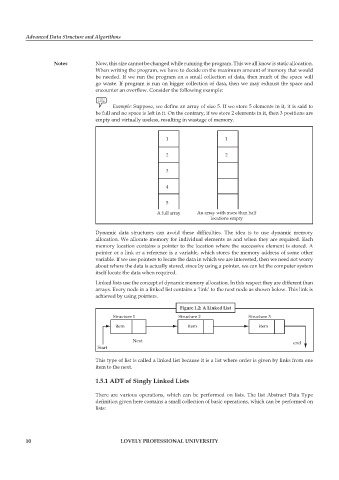
Example: Suppose, we define an array of size 5. If we store 5 elements in it, it is said to
be full and no space is left in it. On the contrary, if we store 2 elements in it, then 3 positions are
empty and virtually useless, resulting in wastage of memory.
1 1
2 2
3
4
5
A full array An array with more than half
locations empty
Dynamic data structures can avoid these difficulties. The idea is to use dynamic memory
allocation. We allocate memory for individual elements as and when they are required. Each
memory location contains a pointer to the location where the successive element is stored. A
pointer or a link or a reference is a variable, which stores the memory address of some other
variable. If we use pointers to locate the data in which we are interested, then we need not worry
about where the data is actually stored, since by using a pointer, we can let the computer system
itself locate the data when required.
Linked lists use the concept of dynamic memory allocation. In this respect they are different than
arrays. Every node in a linked list contains a ‘link’ to the next node as shown below. This link is
achieved by using pointers.
Figure 1.2: A Linked List
Structure 1 Structure 2 Structure 3
item item item
Next end
Start
This type of list is called a linked list because it is a list where order is given by links from one
item to the next.
1.5.1 ADT of Singly Linked Lists
There are various operations, which can be performed on lists. The list Abstract Data Type
definition given here contains a small collection of basic operations, which can be performed on
lists:
10 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY