Page 181 - DCAP605_ADVANCED_DATA_STRUCTURE_AND_ALGORITHMS
P. 181
Advanced Data Structure and Algorithms
Notes
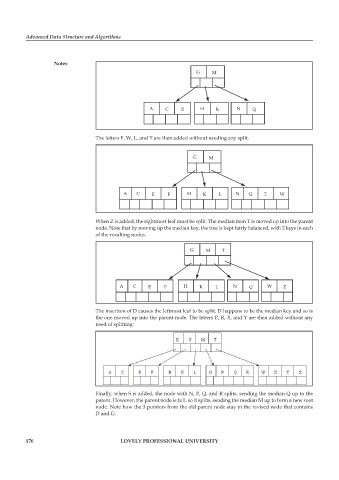
G M
A C E H K N Q
The letters F, W, L, and T are then added without needing any split.
G M
A C E F H K L N Q T W
When Z is added, the rightmost leaf must be split. The median item T is moved up into the parent
node. Note that by moving up the median key, the tree is kept fairly balanced, with 2 keys in each
of the resulting nodes.
G M T
A C E F H K L N Q W Z
The insertion of D causes the leftmost leaf to be split. D happens to be the median key and so is
the one moved up into the parent node. The letters P, R, X, and Y are then added without any
need of splitting:
Finally, when S is added, the node with N, P, Q, and R splits, sending the median Q up to the
parent. However, the parent node is full, so it splits, sending the median M up to form a new root
node. Note how the 3 pointers from the old parent node stay in the revised node that contains
D and G.
176 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY