Page 64 - DCAP605_ADVANCED_DATA_STRUCTURE_AND_ALGORITHMS
P. 64
Unit 3: Stacks
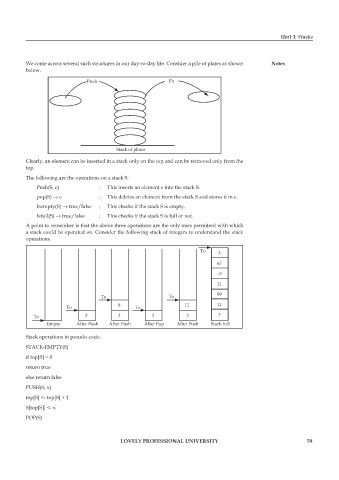
We come across several such structures in our day-to-day life. Consider a pile of plates as shown Notes
below.
Push Po
Stack of plates
Clearly, an element can be inserted in a stack only on the top and can be retrieved only from the
top.
The following are the operations on a stack S:
Push(S, e) : This inserts an element e into the stack S.
pop(S) Æ e : This deletes an element from the stack S and stores it in e.
Isempty(S) Æ true/false : This checks if the stack S is empty.
Isfull(S) Æ true/false : This checks if the stack S is full or not.
A point to remember is that the above three operations are the only ones permitted with which
a stack could be operated on. Consider the following stack of integers to understand the stack
operations.
To 3
67
–5
11
To To 89
To 8 To 11 11
To 3 3 3 3 3
Empty After Push After Push After Pop After Push Stack full
Stack operations in pseudo-code:
STACK-EMPTY(S)
if top[S] = 0
return true
else return false
PUSH(S, x)
top[S] <- top[S] + 1
S[top[S]] <- x
POP(S)
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 59