Page 174 - DCAP311_DCAP607_WIRELESS_NETWORKS
P. 174
Wireless Networks
Notes to a printer, for example, or to synchronize a personal digital assistant with your computer.
Bluetooth can also be used to share Internet access between devices, and therefore also plays a
part in the many technologies that can contribute to a WAN network, more properly known as
a WAN.
!
Caution Except for large organizations that can afford to put up their own satellites or string
their own cables across long distances, wide area networks use a public carrier such as a
phone company to carry communications. Commonly used wireless WAN technologies
include packet radio, cellular telephone, and satellite.
11.1.1 Packet Radio WANs
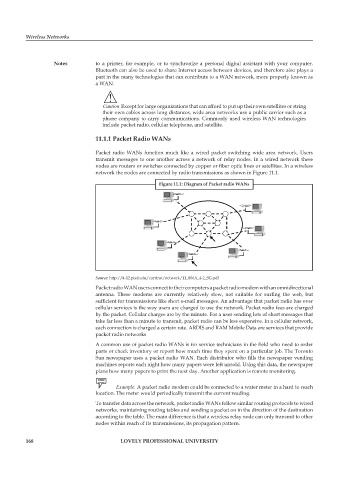
Packet radio WANs function much like a wired packet switching wide area network. Users
transmit messages to one another across a network of relay nodes. In a wired network these
nodes are routers or switches connected by copper or fiber optic lines or satellites. In a wireless
network the nodes are connected by radio transmissions as shown in Figure 11.1.
Figure 11.1: Diagram of Packet radio WANs
Source: http://k-12.pisd.edu/currinst/network/11_806A_4-2_SG.pdf
Packet radio WAN users connect to their computers a packet radio modem with an omnidirectional
antenna. These modems are currently relatively slow, not suitable for surfing the web, but
sufficient for transmissions like short e-mail messages. An advantage that packet radio has over
cellular services is the way users are charged to use the network. Packet radio fees are charged
by the packet. Cellular charges are by the minute. For a user sending lots of short messages that
take far less than a minute to transmit, packet radio can be less expensive. In a cellular network,
each connection is charged a certain rate. ARDIS and RAM Mobile Data are services that provide
packet radio networks
A common use of packet radio WANs is for service technicians in the field who need to order
parts or check inventory or report how much time they spent on a particular job. The Toronto
Sun newspaper uses a packet radio WAN. Each distributor who fills the newspaper vending
machines reports each night how many papers were left unsold. Using this data, the newspaper
plans how many papers to print the next day. Another application is remote monitoring.
Example: A packet radio modem could be connected to a water meter in a hard to reach
location. The meter would periodically transmit the current reading.
To transfer data across the network, packet radio WANs follow similar routing protocols to wired
networks, maintaining routing tables and sending a packet on in the direction of the destination
according to the table. The main difference is that a wireless relay node can only transmit to other
nodes within reach of its transmissions, its propagation pattern.
168 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY