Page 178 - DCAP311_DCAP607_WIRELESS_NETWORKS
P. 178
Wireless Networks
Notes moving so fast that they would pass through smaller cells too quickly. Smaller cells are used
in more densely populated urban areas. PCS (Personal Communications Service) is a popular
digital cellular WAN that uses very small cells that are no more than 10 kilometers across.
Example: The Omnipoint PCS network for the greater New York City area uses over 500
cell sites to cover the 161,300-square-kilometer area.
At the center of each cell is a tower called the base station that holds the antennas, and some
switching equipment. Each base station uses carefully chosen frequencies that will not interfere
with adjacent cells. Each cell is grouped with seven other cells in an organization called a cluster.
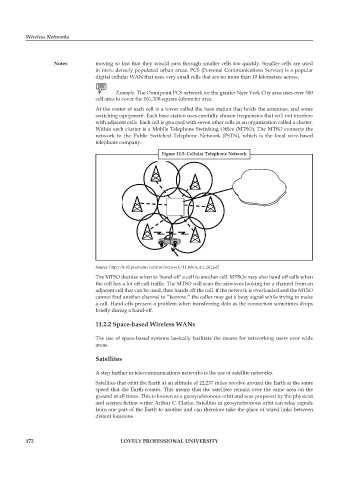
Within each cluster is a Mobile Telephone Switching Office (MTSO). The MTSO connects the
network to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), which is the local wire-based
telephone company.
Figure 11.5: Cellular Telephone Network
Source: http://k-12.pisd.edu/currinst/network/11_806A_4-2_SG.pdf
The MTSO decides when to ‘hand-off’ a call to another cell. MTSOs may also hand off calls when
the cell has a lot off call traffic. The MTSO will scan the airwaves looking for a channel from an
adjacent cell that can be used, then hands off the call. If the network is overloaded and the MTSO
cannot find another channel to “borrow,” the caller may get a busy signal while trying to make
a call. Hand-offs present a problem when transferring data as the connection sometimes drops
briefly during a hand-off.
11.2.2 Space-based Wireless WANs
The use of space-based systems basically facilitate the means for networking users over wide
areas.
Satellites
A step further in telecommunications networks is the use of satellite networks.
Satellites that orbit the Earth at an altitude of 22,237 miles revolve around the Earth at the same
speed that the Earth rotates. This means that the satellites remain over the same area on the
ground at all times. This is known as a geosynchronous orbit and was proposed by the physicist
and science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke. Satellites in geosynchronous orbit can relay signals
from one part of the Earth to another and can therefore take the place of wired links between
distant locations.
172 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY