Page 42 - DCAP311_DCAP607_WIRELESS_NETWORKS
P. 42
Wireless Networks
Notes One (ASN.1), with capabilities such as converting an EBCDIC-coded text file to an ASCII-
coded file, or serialization of objects and other data structures from and to XML.
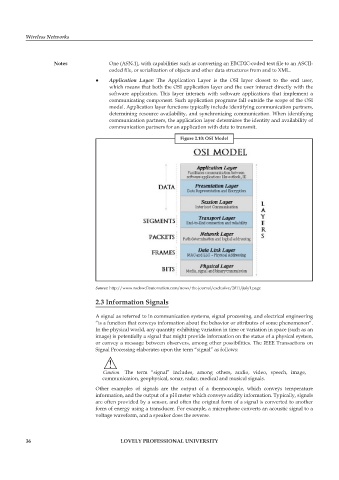
z z Application Layer: The Application Layer is the OSI layer closest to the end user,
which means that both the OSI application layer and the user interact directly with the
software application. This layer interacts with software applications that implement a
communicating component. Such application programs fall outside the scope of the OSI
model. Application layer functions typically include identifying communication partners,
determining resource availability, and synchronizing communication. When identifying
communication partners, the application layer determines the identity and availability of
communication partners for an application with data to transmit.
Figure 2.10: OSI Model
Source: http://www.rockwellautomation.com/news/the-journal/exclusive/2011/july1.page
2.3 Information Signals
A signal as referred to in communication systems, signal processing, and electrical engineering
“is a function that conveys information about the behavior or attributes of some phenomenon”.
In the physical world, any quantity exhibiting variation in time or variation in space (such as an
image) is potentially a signal that might provide information on the status of a physical system,
or convey a message between observers, among other possibilities. The IEEE Transactions on
Signal Processing elaborates upon the term “signal” as follows:
!
Caution The term “signal” includes, among others, audio, video, speech, image,
communication, geophysical, sonar, radar, medical and musical signals.
Other examples of signals are the output of a thermocouple, which conveys temperature
information, and the output of a pH meter which conveys acidity information. Typically, signals
are often provided by a sensor, and often the original form of a signal is converted to another
form of energy using a transducer. For example, a microphone converts an acoustic signal to a
voltage waveform, and a speaker does the reverse.
36 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY