Page 106 - DCAP608_REAL TIME SYSTEMS
P. 106
Unit 10: Working of Clock-driven Scheduling
Notes
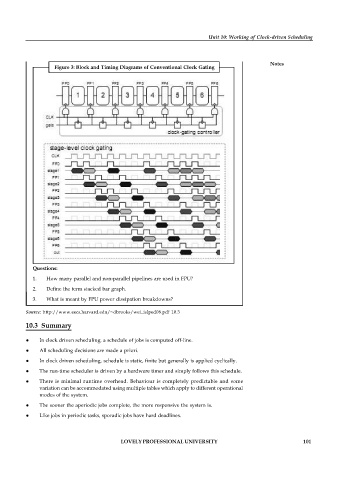
Figure 3: Block and Timing Diagrams of Conventional Clock Gating
Questions:
1. How many parallel and non-parallel pipelines are used in FPU?
2. Define the term stacked bar graph.
3. What is meant by FPU power dissipation breakdowns?
Source: http://www.eecs.harvard.edu/~dbrooks/wei_islped08.pdf 10.3
10.3 Summary
In clock driven scheduling, a schedule of jobs is computed off-line.
All scheduling decisions are made a priori.
In clock driven scheduling, schedule is static, finite but generally is applied cyclically.
The run-time scheduler is driven by a hardware timer and simply follows this schedule.
There is minimal runtime overhead. Behaviour is completely predictable and some
variation can be accommodated using multiple tables which apply to different operational
modes of the system.
The sooner the aperiodic jobs complete, the more responsive the system is.
Like jobs in periodic tasks, sporadic jobs have hard deadlines.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 101