Page 139 - DCAP608_REAL TIME SYSTEMS
P. 139
Real Time Systems
Notes 14.1 Sufficient Schedulability Conditions for the RM and DM
Algorithms
Time-demand analysis method requires the periods and execution times of all the tasks in an
application system to determine whether the system is schedulable.
Before we have completed the design of the application system, some of these parameters may
not be known.
Sufficient Schedulability Conditions for the RM and DM Algorithms are:
1. Schedulable Utilization of the RM Algorithm for Tasks with Di= pi.
2. Schedulable Utilization of RM Algorithms as Functions of Task Parameters
3. Schedulable Utilization of Fixed Priority Tasks with Arbitrary Relative Deadlines
4. Schedulable Utilization of the RM Algorithm for Multi-frame Tasks
14.1.1 Schedulable Utilization of the RM (Di= pi)
Theorem: A system of n independent, preemptible periodic tasks with relative deadlines equal
to their respective periods can be feasibly scheduled on a processor according to the RM algorithm
1/n
if its total utilization U is less than or equal to U (n) = n(2 – 1).
RM
Did u know? U (n) is the schedulable utilization of the RM algorithm when Di= pi for all.
RM
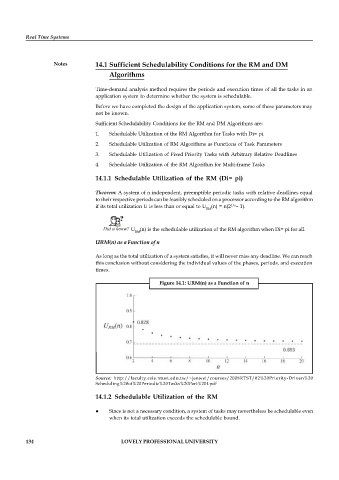
URM(n) as a Function of n
As long as the total utilization of a system satisfies, it will never miss any deadline. We can reach
this conclusion without considering the individual values of the phases, periods, and execution
times.
Figure 14.1: URM(n) as a Function of n
Source: http://faculty.csie.ntust.edu.tw/~jenwei/courses/2008RTST/02%20Priority-Driven%20
Scheduling%20of%20Periodic%20Tasks%20Part%20I.pdf
14.1.2 Schedulable Utilization of the RM
Since is not a necessary condition, a system of tasks may nevertheless be schedulable even
when its total utilization exceeds the schedulable bound.
134 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY