Page 160 - DCAP403_Operating System
P. 160
Unit 8: File Management
8.9.3 Indexed Allocation Notes
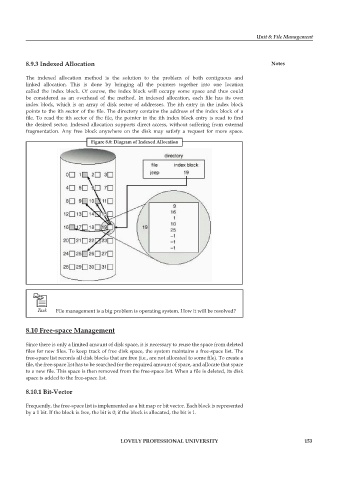
The indexed allocation method is the solution to the problem of both contiguous and
linked allocation. This is done by bringing all the pointers together into one location
called the index block. Of course, the index block will occupy some space and thus could
be considered as an overhead of the method. In indexed allocation, each file has its own
index block, which is an array of disk sector of addresses. The ith entry in the index block
points to the ith sector of the file. The directory contains the address of the index block of a
file. To read the ith sector of the file, the pointer in the ith index block entry is read to fi nd
the desired sector. Indexed allocation supports direct access, without suffering from external
fragmentation. Any free block anywhere on the disk may satisfy a request for more space.
Figure 8.8: Diagram of Indexed Allocation
Task File management is a big problem is operating system. How it will be resolved?
8.10 Free-space Management
Since there is only a limited amount of disk space, it is necessary to reuse the space from deleted
files for new files. To keep track of free disk space, the system maintains a free-space list. The
free-space list records all disk blocks that are free (i.e., are not allocated to some file). To create a
file, the free-space list has to be searched for the required amount of space, and allocate that space
to a new file. This space is then removed from the free-space list. When a file is deleted, its disk
space is added to the free-space list.
8.10.1 Bit-Vector
Frequently, the free-space list is implemented as a bit map or bit vector. Each block is represented
by a 1 bit. If the block is free, the bit is 0; if the block is allocated, the bit is 1.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 153