Page 161 - DCAP403_Operating System
P. 161
Operating System
Notes
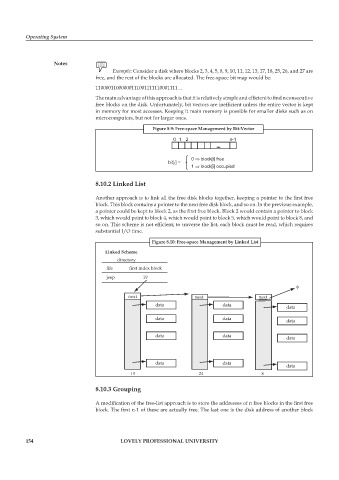
Example: Consider a disk where blocks 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 17, 18, 25, 26, and 27 are
free, and the rest of the blocks are allocated. The free-space bit map would be:
11000011000000111001111110001111…
The main advantage of this approach is that it is relatively simple and effi cient to find n consecutive
free blocks on the disk. Unfortunately, bit vectors are inefficient unless the entire vector is kept
in memory for most accesses. Keeping it main memory is possible for smaller disks such as on
microcomputers, but not for larger ones.
Figure 8.9: Free-space Management by Bit-Vector
01 2 n-1
...
0 block[i] free
bit[i] =
1 block[i] occupied
8.10.2 Linked List
Another approach is to link all the free disk blocks together, keeping a pointer to the fi rst free
block. This block contains a pointer to the next free disk block, and so on. In the previous example,
a pointer could be kept to block 2, as the first free block. Block 2 would contain a pointer to block
3, which would point to block 4, which would point to block 5, which would point to block 8, and
so on. This scheme is not efficient; to traverse the list, each block must be read, which requires
substantial I/O time.
Figure 8.10: Free-space Management by Linked List
Linked Scheme
directory
file first index block
jeep 19
F
next next next
data data
data
data data
data
data data
data
data data
data
8.10.3 Grouping
A modification of the free-list approach is to store the addresses of n free blocks in the fi rst free
block. The first n-1 of these are actually free. The last one is the disk address of another block
154 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY