Page 270 - DCAP403_Operating System
P. 270
Unit 13: Case Study: Linux
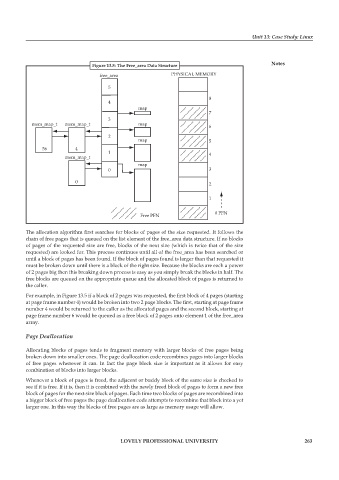
Figure 13.5: The Free_area Data Structure Notes
free_area PHYSICAL MEMORY
5
8
4
map
7
3
mem_map_t mem_map_t map
6
2
map 5
56 4
1 4
mem_map_t
map
0 3
0 2
1
0 PFN
Free PFN
The allocation algorithm first searches for blocks of pages of the size requested. It follows the
chain of free pages that is queued on the list element of the free_area data structure. If no blocks
of pages of the requested size are free, blocks of the next size (which is twice that of the size
requested) are looked for. This process continues until all of the free_area has been searched or
until a block of pages has been found. If the block of pages found is larger than that requested it
must be broken down until there is a block of the right size. Because the blocks are each a power
of 2 pages big then this breaking down process is easy as you simply break the blocks in half. The
free blocks are queued on the appropriate queue and the allocated block of pages is returned to
the caller.
For example, in Figure 13.5 if a block of 2 pages was requested, the first block of 4 pages (starting
at page frame number 4) would be broken into two 2 page blocks. The first, starting at page frame
number 4 would be returned to the caller as the allocated pages and the second block, starting at
page frame number 6 would be queued as a free block of 2 pages onto element 1 of the free_area
array.
Page Deallocation
Allocating blocks of pages tends to fragment memory with larger blocks of free pages being
broken down into smaller ones. The page deallocation code recombines pages into larger blocks
of free pages whenever it can. In fact the page block size is important as it allows for easy
combination of blocks into larger blocks.
Whenever a block of pages is freed, the adjacent or buddy block of the same size is checked to
see if it is free. If it is, then it is combined with the newly freed block of pages to form a new free
block of pages for the next size block of pages. Each time two blocks of pages are recombined into
a bigger block of free pages the page deallocation code attempts to recombine that block into a yet
larger one. In this way the blocks of free pages are as large as memory usage will allow.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 263