Page 67 - DCAP403_Operating System
P. 67
Operating System
Notes over any other thread’s stacks. This structure does not provide protection between threads. Such
protection, however, should not be necessary. Whereas processes may originate from different
users, and may be hostile to one another, only a single user can own an individual task with
multiple threads. The threads, in this case, probably would be designed to assist one another, and
therefore would not require mutual protection.
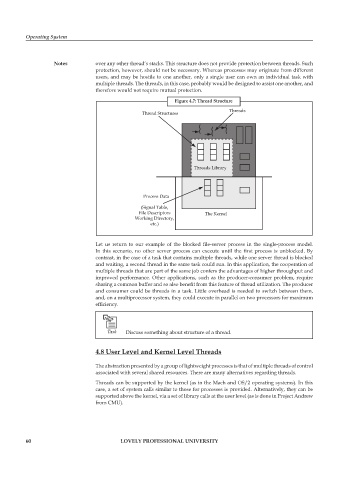
Figure 4.7: Thread Structure
Threads
Thread Structures
Threads Library
Process Data
(Signal Table,
File Descriptors The Kernel
Working Directory,
etc.)
Let us return to our example of the blocked file-server process in the single-process model.
In this scenario, no other server process can execute until the first process is unblocked. By
contrast, in the case of a task that contains multiple threads, while one server thread is blocked
and waiting, a second thread in the same task could run. In this application, the cooperation of
multiple threads that are part of the same job confers the advantages of higher throughput and
improved performance. Other applications, such as the producer-consumer problem, require
sharing a common buffer and so also benefit from this feature of thread utilization. The producer
and consumer could be threads in a task. Little overhead is needed to switch between them,
and, on a multiprocessor system, they could execute in parallel on two processors for maximum
effi ciency.
Task Discuss something about structure of a thread.
4.8 User Level and Kernel Level Threads
The abstraction presented by a group of lightweight processes is that of multiple threads of control
associated with several shared resources. There are many alternatives regarding threads.
Threads can be supported by the kernel (as in the Mach and OS/2 operating systems). In this
case, a set of system calls similar to those for processes is provided. Alternatively, they can be
supported above the kernel, via a set of library calls at the user level (as is done in Project Andrew
from CMU).
60 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY